Introduction
X.500 is basically used to query information about the person's information (such as postal address, phone number, email address, etc.). It can be: the department name and the national name of the institution. X.500 Directory Services is a standard way for developing a unit (or organization) internal personnel electronic directory. This directory can be part of the global catalog, anyone in the world can access the Internet to query the directory. This directory is sometimes referred to as the global user information database directory, and its idea comes to people's names, departments and units in the user interface. Many companies and organizations have established X.500 directories.
This catalog organizes the same "root" directory with a "tree" structure, including: country, unit, department and individual. Two well-known X.500 directories are also the largest X.500 directory, which is an INTERNIC for managing domain names and stores the ESNET in the United States.
The directory system agent (DSA) is called a directory system agent (DSA) in X.500, and a DSA represents one or more units (or organizations), while the DSA is connected in a directory information tree (DIT).
X.500 is a directory access protocol defined by ITU-T and ISO, providing an electronic catalog on an organization member that enables anyone within the world access to Internet access to this directory.
In the X.500 directory structure, through the directory access protocol DAP, the client query and receive a response from one or more servers from the server directory service, thereby implementing the server and client Communication control.
Directory System Agent DSA refers to a database for storing directory information. The database uses a hierarchical format with a fast and efficient search function. DSAS is connected to the directory information tree DIT. Directory User Agent DUA is a user interface program for accessing one or more DSAS. DUAS includes WHOIS, finder finger, and providing a related program that is a graphical user interface.
Directory System Protocol DSP mainly controls two or more directory system agency, directory user agent, and interactive operations between directory system agents. The specific implementation process is that the end user can access the information in the directory without knowing the exact location of a particular information.
X.500 Protocol
In the X.500 protocol, the local X.500 client is also called a directory user agent (DUA). The easiest way to get the X.500 customer program is to obtain from the public software library through FTP, and the X.500 client is generally based on three ways: the command line-based user interface; menu-driven user interface; The user interface of the X-Windows system.
The registration name of the command line user interface is: DE, DISH, FRED;
The registration name of the user interface is: SD (previously: widget);The registration name of the user interface is: XDI, XLookup (XLU), Pool.
The functions provided by these directory user agents are different, and some provide only basic query functions, and some support all X.500 features.
X.500 directory structure
In the X.500 directory structure, the client queries and receives responses from one or more servers from the server directory service
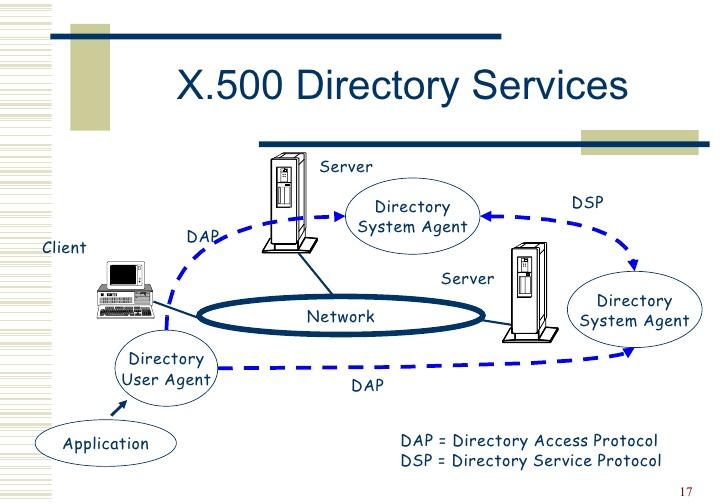
Directory Access Protocol (DAP) Controls between servers and clients.
Directory System Agent (DSA: Directory System Agent) refers to a database for storing directory information. The database uses a hierarchical format to provide fast and efficient search capabilities. The DSA is connected to the directory information tree (DIT: DIRECTORY INFORMATION TREE).
Directory User Agent (DUA: Directory User Agent) is a user interface program for accessing one or more DSAs. DUA includes WHOIS, Finder (Finger), and related programs that provide graphical user interfaces.
Directory System Protocol (DSP: Directory System Protocol) mainly controls two or more directory system agencies, directory user agent and directory system agents interactive operations. The specific implementation process is that the end user can access information in the directory in the case where the specific location of a particular information is not known.
X.500 Purpose
INTERSYSTEM COMMUNICATION: This is, the two Exchange is mobile. Autherticaion Service: AD login is apparent, when the user provides a SID, then the server gives back the design process of a token
directory: 1. Determine the scope: Decide the object class supported by the directory ( Like object-oriented ideas). For network systems, including user accounts, groups, printers, servers, etc., and even routes, switches. 2. Determine attribute:
account name, account phone, account. . . . . Waiting for attribute 3, create a directory, build a database: object, after the property is clear, you should consider how these data is stored, and the user is simple.
Directory structure:
Directory structure is a hierarchical structure, similar to the structure of DOS or Linux, indicating that the structure of the directory
c is represented by COUNTY OU means Organization Unit L represents Location
C, OU, L, represents a container, which uses to organize database objects. Note that it is not a file in the container, but the characteristics of Object
X.500
X.500 mainly has the following characteristics
1. Dispersion maintenance ( Decentralized maintenance: Each site running X.500 is only responsible for its local directory section, so you can update and maintain your operation immediately.
2. Powerful search performance: X.500 provides powerful search capabilities to support any complex queries established by users.
3. Single Global Namespace: Similar to DNS, X.500 provides users with single-same namespace (Single Homogeneous Namespace). Compared with DNS, the namespace of X.500 is more flexible and easy to expand.
4. Structured Information Structure: The information structure is defined in the X.500 directory, allowing local extensions.
5. Standards-based Directory Service: Since the X.500 can be used to establish a standard directory, in a sense, request application directory information (electronic The application of the message, resource auto-distributor, and specific directory tools can access important and valuable information.
is criticized due to the implementation of X.500. In order to solve this problem, Michigan University has introduced a more simple TCP / IP-based DAP version, which is a lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP: Lightweight Directory Protocol, mainly for the Internet. LDAP and DAP have many similar basic functions, and it can also be used to query private directorys and open data on the X.500 directory. In the past few years, most of the major emails and directory service software vendors have shown great interest in LDAP, and LDAP has quickly developed into the directory protocol standards for the facts of the Internet.
