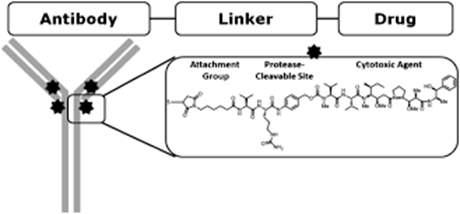
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are innovative therapeutic agents designed to deliver cytotoxic drugs directly to cancer cells, sparing healthy tissue. Comprised of an antibody linked to a potent drug via a linker, ADCs leverage the specificity of antibodies to bind to unique cancer cell antigens. Once the ADC binds to its target cell, it's internalized, and the cytotoxic drug is released to exert its therapeutic action. This ensures that the potent drug selectively targets cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Metabolism and ADCs: The Central Role
The role of metabolism in the functionality of ADCs cannot be understated. ADC metabolism significantly determines the therapeutic window of an ADC – that is, the range of drug doses that can treat the disease effectively without causing undue harm. ADCs metabolize into various species, each with a distinct pharmacokinetic profile. These species can have therapeutic and safety implications, thus making the understanding of ADC metabolism crucial. ADCs mainly undergo metabolism inside the target cell post-internalization. Within the cell, various processes break down the ADC to release the cytotoxic drug. Nonetheless, ADCs also face metabolic processes in the bloodstream, which can influence their efficacy and safety.
Linkers, Drugs, and Catabolism
A critical aspect of ADCs is the stability of the linker that attaches the drug to the antibody. A stable linker ensures the drug remains affixed to the antibody until the ADC reaches its intended target: the cancer cell. On the contrary, unstable linkers might release the drug prematurely, leading to unintended exposure to healthy cells. Furthermore, once an ADC is inside a cell, the drug's release mechanism can differ. Some ADCs are tailored to discharge the drug in the endosomes' acidic environment, while others depend on cellular enzymes to cleave the linker, setting the drug free. Post-drug release, the residual antibody fragments, and possible linker remnants undergo catabolic degradation within the cell. The effects of these metabolites, too, need understanding in terms of safety and efficacy.
Recirculation and Its Effects
Beyond initial metabolism, some ADC metabolites can navigate their way out of the target cell and re-enter the bloodstream. Such recirculating metabolites might extend the ADC's action or, in some instances, lead to unintended side effects due to interactions with other cells or molecules in the bloodstream.
Clinical Implications of ADC Metabolism
The metabolism of ADCs has direct implications for their therapeutic applications. A deep understanding of metabolic pathways can lead researchers to design ADCs with optimized therapeutic windows. This can be achieved by selecting linkers that release drugs optimally or by opting for drugs with preferable metabolic profiles. Side effects are also a significant concern. Premature drug release or metabolite interactions with non-target cells can result in off-target effects. A study of ADC metabolism can lead to strategies that minimize such adverse outcomes. Additionally, knowledge of how ADCs metabolize can provide insights into potential mechanisms of drug resistance. If cancer cells develop strategies to degrade ADCs faster or hinder drug release, it could diminish the treatment's effectiveness.

The Road Ahead
ADCs symbolize a major advancement in targeted cancer therapy. They hold the potential for treatments that are both effective and accompanied by fewer side effects. The complex world of ADC metabolism is ripe for exploration, and as we unravel its intricacies, we pave the way for next-generation ADCs. These novel ADCs can promise improved therapeutic outcomes, fewer side effects, and strategies to counteract potential resistance mechanisms. To reiterate, ADCs offer a promising direction in cancer therapy. Yet, understanding their metabolism is paramount for maximizing their benefits and ensuring their safe and effective use in patients. A deeper dive into ADC metabolism will undoubtedly lead to more targeted and potent cancer treatments.
