Concept originates
The thermodynamic system is influenced by the external boundary, from a variation of a balanced state to another, referred to as the thermodynamic process, referred to as the process. At any time of the process, the status of the system is of course not a balance state. For example, when the gas in which the piston is compressed in the gas cylinder, the volume, density, temperature or pressure of the gas will change, at any time, the density, pressure, and temperature of the gas in the process, and the temperature is not exactly the same. The gas density close to the surface of the piston is large, and the pressure is also large, the temperature is also higher. In thermodynamics, in order to use the nature of the system to be in equilibrium to study the law, the concept of quasi-static process is introduced.
concept
The quasi-static process is such a process. At any time during the process, the system is infinitely close to the balance state, and thus the state of any time system can be processed as a balance state. That is, the quasi-static process is a process composed of a series of balanced balances in turn.
The quasi-static process is an ideal process. The slower the actual process, the smaller the change in the state of the system, the closer the state of the system, the closer the balance state. When the actual process is infinitely slow, the state of the system is unlimited in the state of the system, and the process is a quasi-static process. Therefore, the quasi-static process is the limit of the actual process in unlimited slowness. Here, "Unlimited", it should be understood from the relative meaning. If a system is initially in a non-equilibrium state, a transition time is relaxed when it is transitioned to a balance state. In a practical process, if the system's status occurs than the time required to be more than a relaxation time, the system has a sufficient time to achieve a balance state when observing at any time. Such a process can be processed as a static process. For example, the gas in the original cylinder is in a balanced state, and the time required to reach the balance state, that is, the relaxation time, about 10 ^ -3s or smaller, if it is compressed in the experiment, it is 1s, this Time is 10 ^ 3 times the relaxation time, and the compression process of the gas can be considered as quasi-static process. The actual internal combustion engine cylinder gas experiences that the compression time is about 10 ^ -2 s, which is also more than 10 times the above relaxation time. In theory, when this compression process is preliminary, it also processes it as a quasi-static process.
Representation method
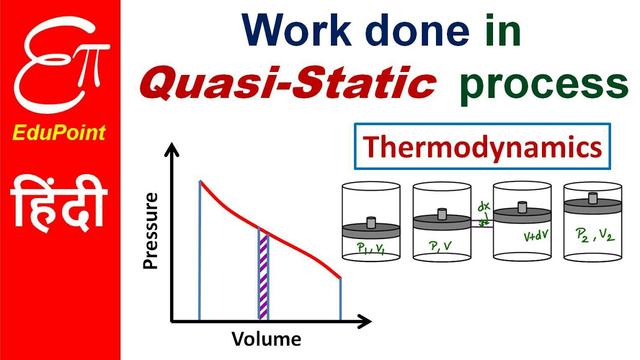
The quasi-static process can be represented by a state diagram of the system, such as a curve in the P-V map (or P-T map, V-T map). In the reproduction diagram, any point represents a balance state of the system, so a curve represents a quasi-static process consisting of a series of balanced states, such a curve is called a process curve. The equation of this curve is called a process equation, as shown in Figure 1 is a common concentrated equivalent process curve.
For quasi-static processes, the size of the work can be calculated directly by the system's state parameters. Mechanical work is commonly discussed in the system to remain stationary.
