Basicinformation
Principlesofpacing
Thepulsegeneratorregularlyemitsapulsecurrentofacertainfrequency,whichistransmittedtotheelectrodesthroughwiresandelectrodesThecontactedmyocardium(atriumorventricle)causeslocalmyocardialcellstobeexcitedbyexternalelectricalstimulation,andconductstothesurroundingmyocardiumthroughthegapjunctionorintercalarydiscconnectionbetweenthecells,whichleadstotheexcitementoftheentireatriumorventricleandthusproducescontractionactivity.Whatneedstobeemphasizedisthatthemyocardiummusthavethefunctionsofexcitation,conduction,andcontraction,sothattheheartcanperformitsrolewithpacing.
Thecompositionofthepacingsystem
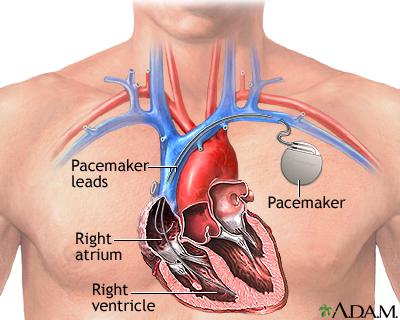
Theartificialheartpacingsystemmainlyincludestwoparts:pulsegeneratorandelectrodelead.Thepulsegeneratorisoftencalledapacemakeralone.Inadditiontotheabove-mentionedpacingfunctions,thepacingsystemalsohasthesensingfunctionofreturningtheheart'sownelectricalactivitytothepulsegenerator.
Thepacemakerismainlycomposedofapowersource(thatis,abattery,andnowmainlyusesalithium-iodinebattery)andanelectroniccircuitprocess,whichcangenerateandoutputelectricalpulses.
Theelectrodeleadisaconductivemetalwirewrappedwithaninsulatinglayer.Itsfunctionistotransmittheelectricalpulseofthepacemakertotheheart,andtransmittheheart'sintracavityelectrocardiogramtothesensingcircuitofthepacemaker.
Indicationsforartificialcardiacpacing
Artificialcardiacpacingisdividedintotemporaryandpermanent,whichhavedifferentindications.
1.Temporarycardiacpacingindications
TemporarycardiacpacingisatemporaryortemporarySexualartificialcardiacpacing.Thepacingleadisgenerallyplacedfornomorethan2weeks,andthepacemakersareplacedoutsidethebody,andthepacingleadiswithdrawnimmediatelyafterthepurposeofdiagnosis,treatmentandpreventionisachieved.Ifyoustillneedtocontinuepacingtherapy,youshouldconsiderinsertingapermanentpacemaker.Anypatientwithsymptomaticorbradycardiathatcauseshemodynamicchangesisthesubjectoftemporarycardiacpacing.Thepurposeoftemporarycardiacpacingisusuallydividedintotreatment,diagnosis,andprevention.
(1)Therapeuticaspects
1)OnsetofAl-Sissyndrome:variousreasons(acutemyocardialinfarction,acutemyocarditis,digitalisoranti-Arrhythmiadrugs,poisoning,electrolytedisturbances,etc.)causedbyatrioventricularblock,sinusnodefailure,andtheoccurrenceofcardiacarrestandA-Ssyndromearetheabsoluteindicatorsofemergencytemporarycardiacpacing.Levy.
2)Transitionofpatientswithunstableheartrhythmbeforetheplacementofapermanentpacemaker.
3)Third-degreeatrioventricularblockcausedbyopenheartsurgery.
4)Torsadedepointesand/orpersistentventriculartachycardiainducedbybradycardiathatareineffectiveindrugtherapy.
(2)Diagnosis
Asanauxiliarymethodforsomeclinicaldiagnosisandelectrophysiologicalexamination.Forexample,judge:①sinusnodefunction;②atrioventricularnodefunction;③pre-excitationsyndrometype;④reentrantarrhythmia;⑤effectofantiarrhythmicdrugs.
(3)Prevention
1)High-riskpatientswhoareexpectedtohaveobviousbradycardiaCommonacutemyocardialSomepatientswithinfarctbradyarrhythmiasandcardiacconductionsystemdysfunctionareplannedtoundergomajorsurgeryandinterventionalcardiacsurgery,andpatientswithtachyarrhythmiasuspectedofsinusnodedysfunctionundergocardioversiontherapy,andtheoriginalleftbundlebranchblockispresentOfpatientsundergoingrightheartcatheterization.
2)PacemakerdependentpatientsTransitionwhenreplacinganewpacemaker.
2.Permanentcardiacpacingindications
Withtheimprovementofpacingengineering,theindicationsforpacingtherapyhavegraduallyexpanded.Themainpurposeofimplantingapacemakerintheearlyyearswastosavethelifeofthepatient.Atpresent,itstillincludesrestoringthepatient'sworkingabilityandqualityoflife.Thecurrentmainindicationscanbesimplysummarizedassevereheartdiseasessuchasslowheartbeat,weakheartcontraction,andcardiacarrest.In2012,theAmericanSocietyofCardiology/AmericanHeartAssociation/AmericanHeartRhythmAssociationre-formulatedtheguidelinesforimplantingcardiacpacemakers.
(1)TypeIindicationsmainlyinclude
1)Sinusnodeinsufficiency①RecordedsymptomsSinusnodedysfunction,includingsinusarrestthatoftencausessymptoms.②Patientswithsymptomaticchronosexuality.③Becauseofcertaindiseases,certaindrugsmustbeused,andthesedrugscancausesinusbradycardiaandproducesymptoms.
2)Adultswithacquiredatrioventricularblock(AVB)①AnyblocksitewithⅢdegreeAVBandhighAVB,complicatedbysymptomaticbradycardia(includingHeartfailure)orventriculararrhythmiasecondarytoAVB.②Long-termuseofdrugsforthetreatmentofotherarrhythmiasorotherdiseases,andthedrugcancausethird-degreeAVBandhigh-levelAVB(regardlessoftheblocklocation),andsymptomaticbradycardia.③Asymptomaticpatientswiththird-degreeAVBandhigh-levelAVBatanyblocksiteintheawakestate,wererecordedtohaveacardiacarrestof3secondsorlonger,oranescapeheartratebelow40bpm,oranescaperhythmpacemakerpointThosebelowthesinusnode.④Intheawakestate,thereisoneormorelongpausesofatleast5secondsinthethirddegreeAVBandhighAVBatanyblocksite,asymptomaticatrialfibrillationandbradycardia.⑤Thethird-degreeAVBandhigh-levelAVBofanyblockthatappearsaftercatheterablationoftheatrioventricularnode.⑥Thethird-degreeAVBandhigh-levelAVBofanyblocksitethatcannotberecoveredaftercardiacsurgery.⑦GradeIIIAVBandhighAVBatanyblocksitecausedbyneuromusculardisease,suchasmyotonicmusculardystrophy,Karns-Sayresyndrome(Kearn-Sayresyndrome),pseudohypertrophicmusculardystrophy,peronealsidePatientswithmuscularatrophy.⑧GradeIIAVBwithbradycardiasymptoms,regardlessoftypeorblocklocation.⑨Asymptomaticthird-degreeatrioventricularblockaverageventricularrateatanyblocksiteor>40beats/minwithenlargedheartorabnormalleftventricularfunctionorblockbelowtheatrioventricularnode.⑩DegreeIIorIIIAVBduringexercisewithoutmyocardialischemia.
3)Patientswithchronictwo-branchblock①accompaniedbyhighAVBortransientthird-degreeAVB.②AccompaniedbytypeIIAVB.③Withalternatingbundlebranchblock.
4)Acutemyocardialinfarctionwithatrioventricularblock①AfterST-segmentelevationmyocardialinfarction,continuoussecond-degreeAVBofHis-PurkinjesystemwithalternatingbundlebranchblockOrⅢdegreeAVB;②TransientseverityⅡorⅢdegreeAVBundertheAVBwithbundlebranchblock;
③PersistentandsymptomaticdegreeⅡorⅢAVB.
5)Carotidsinushypersensitivityandcardiacneurogenicsyncope①Spontaneouscarotidarterystimulationandcarotidcompression-inducedventriculararresttime>3srepeatedsyncope.②Patientswithpersistentorsymptomaticbradyarrhythmiaandnohopeofrecoveryafterhearttransplantation.③Longintermittentdependentventriculartachycardia,withorwithoutprolongedQTinterval.
Leftventricularejectionfraction≤35%,completeleftbundlebranchblockandQRS≥150ms,sinusrhythm,cardiacfunctionclassification(NYHA)Ⅱ,ⅢoridealafterdrugtreatmentForNYHAIVheartfailurepatients,CRTorCRT-ICDshouldbeimplanted.
TheindicationsofICDareasfollows:①Ventricularfibrillationorhemodynamicallyunstablepersistentventriculartachycardia(VT),exceptforotherreversiblecauses,survivorsofcardiacarrest;②OrganicHeartdiseaseandspontaneouspersistentVT,nomatterwhetherhemodynamicsarestableornot;③Haveahistoryofsyncope,electrophysiologicalexaminationclearlyinduceshemodynamicallyunstablepersistentVTorventricularfibrillation(VF);④40daysaftermyocardialinfarction,Leftventricularejectionfraction≤35%,NYHAⅡorⅢgrade;⑤Non-ischemicdilatedcardiomyopathy,leftventricularejectionfraction≤35%,NYHAⅡorⅢgrade;⑥Leftventriculardysfunctionbeforemyocardialinfarction,myocardiumAfter40daysofinfarction,leftventricularejectionfraction≤30%,NYHAⅠ;⑦Aftermyocardialinfarction,leftventricularejectionfraction≤40%,non-sustainedVTorelectrophysiologicalexaminationinducedVForsustainedVT.
(2)ClassⅡaindicationsmainlyinclude
1)Sinusnodeinsufficiency①SinusnodefunctionThedisordercausesaheartrateof<40bpm,andthereisclearevidencebetweensymptomsandbradycardia,regardlessofwhetherbradycardiaisrecorded.②Patientswithunexplainedsyncopeandsinusnodedysfunctioninducedbyclinicaldiscoveryorelectrophysiologicalexamination.
2)AdultswithacquiredAVB①Asymptomaticpersistentthird-degreeAVB,escapeheartratelowerthan40bpmwithoutheartenlargement.②Theelectrophysiologicalexaminationrevealedasymptomaticsecond-degreeAVBatorbelowtheHisbundle.③DegreeIorDegreeIIAVBisaccompaniedbyhemodynamicperformancesimilartopacemakersyndrome.④AsymptomatictypeIIAVBandnarrowQRScomplex.However,whentypeIIAVBisaccompaniedbyawideQRScomplex,includingrightbundlebranchblock,theindicationisupgradedtotypeI.
3)Patientswithchronictwo-branchblock①AlthoughithasnotbeenconfirmedthatsyncopeiscausedbyAVB,otherreasons(especiallyventriculartachycardia)canberuledout.②Althoughtherearenoclinicalsymptoms,theelectrophysiologicalexaminationrevealsthattheHVintervalis≥100ms.③Duringelectrophysiologicalexamination,non-physiologicalblockbelowHisbundleinducedbyatrialpacing.
Repetitivesyncope,noexactcarotidarteryirritationevent,high-sensitivitycardiacinhibitionresponsetoventriculararresttime>3seconds,shouldconsiderimplantingapermanentcardiacpacemaker.
Thepacingtreatmentoftachycardiaislimitedtopatientswithsupraventriculartachycardiawhohavefailedcatheterablationand/ordrugtherapy,orwhocannottoleratethesideeffectsofdrugsandhaverecurrentepisodes.
High-riskpatientswithlongQTsyndrome.
CRTorCRT-ICDcanbeimplantedinthefollowingpatientswithheartfailure:①Leftventricularejectionfraction≤35%,completeleftbundlebranchblockandQRSbetween120msand149ms,sinusrhythm,Heartfunctionclassification(NYHA)Ⅱ,ⅢorNYHAⅣheartfailurepatientswhocanbeactiveafteridealdrugtreatment;②Leftventricularejectionfraction≤35%,non-leftbundlebranchblockandQRS≥150ms,sinusrhythm,Heartfunctionclassification(NYHA)II,IIIorNYHAIVheartfailurepatientswhocanbeactiveafteridealdrugtreatment;③Patientswithheartfailurewithleftventricularejectionfraction≤35%combinedwithatrialfibrillationafteridealdrugtreatment,ifventricularrecoveryisneededTheleftventricularejectionfractionislessthanorequalto35%afteridealdrugtreatment,andthedeviceneedstobenewlyinstalledorreplacedandreliesonventricularpacing(40%).
Thereisariskofsuddencardiacdeath(SCD)(mainSCDrisks:historyofcardiacarrest,spontaneouspersistentVT,spontaneousnon-persistentVT,familyhistoryofSCD,syncope,leftventricularthickness≥30mm,duringexerciseAbnormalbloodpressureresponse;possibleSCDrisk:atrialfibrillation,myocardialischemia,leftventricularoutflowtractobstruction,highriskofmutation,andintensecompetitivephysicalactivity)patientswithobstructivehypertrophiccardiomyopathyshouldbeimplantedDDD-ICD.
TherecommendedindicationsforICDareasfollows:①Non-ischemicdilatedcardiomyopathy,significantleftventriculardysfunction,unexplainedsyncope;②Persistentventriculartachycardia,evenifventricularfunctionisnormalorclosetonormal;③PatientswithhypertrophiccardiomyopathyhavemorethanonemajorriskfactorforSCD;
④Patientswitharrhythmogenicrightventriculardysplasia/cardiomyopathyhaveonemajorriskfactorforSCD(includingelectrophysiologicalexamination-inducedVT,ECGMonitorednon-sustainedVT,male,severerightventricularenlargement,extensiverightventricularinvolvement,<5yearsold,leftventricularinvolvement,historyofcardiacarrest,unexplainedsyncope);⑤PatientswithlongQTsyndromearereceivingβSyncopeand/orventriculartachycardiaduringbodyblockers;⑥Patientswaitingforhearttransplantationoutsidethehospital;⑦Brugadasyndromewithsyncope;⑧Brugadasyndromewithventriculartachycardiabutnocardiacarrest;⑨catecholamine-sensitiveventriculartachycardiaPatientsstillhavesyncopeand/orventriculartachycardiaafterusingβ-blockers;⑩Patientswithcardiacsarcoidosis,giantcellmyocarditis,andChagasdisease.
Ofcoursetheguidelinesdonotcoverallclinicalsituations.Foraspecificpatient,theindicationsforpermanentcardiacpacingarenotalwaysclear.Usually,irreversible,symptomaticbradycardiaisthemainindicationforimplantingapermanentpacemaker.Thedoctorinchargeshouldmakethedecisionwhetherornottoimplantapermanentpacemakerbasedonthepatient'sspecificcondition,patient'swishes,andeconomicstatus.
Reasonablechoiceofpacemaker
Whatkindofpacemakertochooseforaspecificpatientisaproblemthatcliniciansoftenface.Theprinciplesareasfollows:
1.Ifthereischronicpersistentatrialfibrillationoratrialquiescence
chooseVVI(R).
2.Sinusnodedysfunction
Ifthereisnoatrioventricularblockortheprobabilityofoccurrenceofatrioventricularblockinthenearfutureislow,chooseAAI(R),otherwisechooseDDD(R).
3.Atrioventricularblock
Ifthereispersistentatrialtachyarrhythmia,chooseVVI(R);②thereissicksinusSyndrome,chooseDDD(R);③Thesinusnodefunctionisnormalortheprobabilityofsinusnodeinsufficiencyisexpectedtobelow,chooseVDDorDDD.
Singleventricularpacingisnolongerrecommended,anddual-chamberpacingincreasesthequalityoflifecorrectedforsurvivalatagenerallyacceptedprice.RegardingthechoiceofimplantingAAIorDDDpacemaker,althoughDDDismoreexpensive,itshouldbeconsideredthatthepatientmaydevelopatrioventricularblock.
Inaddition,itisnecessarytoconsiderthepatient’sage,heartdiseaseandcombineddiseases,economicstatus,andthepatient’soverallgeneralcondition.
(1)Temporarycardiacpacing
Withpercutaneouspacing,transesophagealpacing,transthoracicpacing,thoracicepicardialopeningFivemethodsincludingpacingandtransvenouspacing.Atpresent,choosethelatter.
Usually,femoralvein,subclavianveinorinternaljugularveinpunctureisusedtoinserttemporarypacingleadwires.Displacementofleadwiresismorecommonthanpermanentcardiacpacing.PostoperativeECGmonitoringshouldbestrengthened,includingearlypacingthresholdelevation,changesinperceptionsensitivity,andleaddislocations,especiallythosewhorelyonpacemakers.Inaddition,becausetheelectrodewireisconnectedtotheoutsidethroughthepuncturepoint,itisnecessarytopayattentiontolocalcleaningtoavoidinfection,especiallyforthosewhohavebeenplacedforalongtime.Inaddition,aftertemporarypacingviathefemoralvein,thepatientshouldremaininasupineposition,withthelowerextremityimmobilizedonthesideofthevenipuncture.
(2)Permanentcardiacpacing
Currently,mostoftheendocardialleadwiresareused.Technicalpointsincludeveinselection,wireelectrodefixationandpacemakerembedding.
1)VeinselectionTheveinsthatcanbeusedtoinsertleadwiresareusually:superficialveinsincludecephalicveinandexternaljugularvein,deepveinsincludesubclavianvein,axillaryveinandinternaljugularvein.Usually,thecephalicveinorsubclavianveinontheoppositesideofthehandisthefirstchoice.Ifitisunsuccessful,theinternalorexternaljugularveinshouldbeselected.
2)PlacementoftheleadwiresPlacetheleadwiresintheheartcavitywherepacingisrequired.Passivefixationisgenerallyused,oractivefixationoftheleadwirescanbeused.
3)EmbeddingofpacemakersPacemakersaregenerallyembeddedundertheskinofthechestonthesamesideoftheleadwire.Connecttheelectrodeleadtothepulsegenerator,andputtheextraleadnearthemusclesurfaceandthepacemakerneartheskinintothesubcutaneousbag.
Themethodistoinserttheleadwirefromthearmorveinunderthecollarbone,insertitintothepredeterminedcardiacpacingpositionunderX-rayfluoroscopy,fixitandmeasureit.Then,apacemakerconnectedtotheleadwiresisembeddedinthechest,theskinissutured,andtheoperationcanbecompleted.
(3)Permanentcardiacpacingcomplications
1)ComplicationsrelatedtoimplantationsurgeryMostcomplicationsSuchascarefuloperationduringtheoperationshouldbeabletoeliminate,somearedifficulttocompletelyavoid.Theincidenceiscloselyrelatedtotheexperienceoftheimplantdoctor.
①Arrhythmiausuallydoesnotrequirespecialtreatment.②Localbleedingcanusuallybeabsorbedbyitself.Whenthereisobvioushematomaformation,thebloodcanbesqueezedoutunderstrictasepticconditions.③ComplicationsandtreatmentofsubclavianveinpuncturePneumothorax:Asmallamountofpneumothoraxdoesnotrequireintervention.Whenthepneumothoraxcompressesthelungtissue>30%,itisnecessarytodrawairorplaceadrainagetube.Intothesubclavianarterybymistake:theneedleand(or)theguidewireshouldberemovedandlocalpressureshouldbeappliedtostopthebleeding(donotinsertthedilationtube),usuallywithoutspecialtreatment.④Heartperforationisrare.Treatment:Thecathetershouldbecarefullysprinkledbackintotheheartcavity,andthepatient'sbloodpressureandheartconditionshouldbecloselyobserved.Oncetheperformanceofpericardialtamponadeappears,consideropeningthechestforpericardialdrainageorcardiacrepair.Whencontinuingtoinstalltheelectrode,avoidpositioningattheperforation.⑤Infectionisrare.Treatment:Oncealocalabscessisformed,thereisverylittlechanceofconservativetreatmenttoheal.Itshouldbeincisedanddrainedassoonaspossible,debridethewound,removetheleadwireinthewound,andchooseanewimplantationroute.⑥Diaphragmstimulationisrare.Cancauseintractablehiccups.Itismorecommonwhentheleftventricularleadisimplanted.Treatment:Reducethepacemakeroutputorchangetobipolarpacing.Ifthesymptomspersist,theelectrodepositionshouldbereadjusted.
(4)Complicationsandtreatmentsrelatedtoelectrodeleads
1)ThresholdincreaseTreatment:increasethroughprogramcontrolItcanoutput,andtheelectrodepositionorwireneedstobereplacedifnecessary.
2)ElectrodedislocationandmicrodislocationcanbefoundbyX-rayexaminationwhentheelectrodedislocationandmicrodislocationareobviouslyshifted.X-rayfluoroscopyshowsthattheelectrodetipisstillinplaceinthecaseofmicrodislocation,butitisactuallyPoorcontactoftheinnermembrane.Treatment:usuallyneedtore-surgery,adjusttheelectrodeposition.
3)TheelectrodewireisbrokenortheinsulationlayerisbrokenIftheimpedanceisverylow,considertheinsulationlayerdamage;iftheimpedanceisveryhigh,considertheelectrodewirebreaking.Treatment:Itisoftennecessarytore-implantanewelectrodelead.
(5)Complicationsandtreatmentrelatedtopacemakers
Withtheprogressofengineering,pacemakerssuchaspacemakersthemselvesThefailureofthepacemakerisrare.Theoccasionalpacemakerfailureistheresetofthepacemakerandtheprematureexhaustionofthepacemakerbattery.Pacemaker.
Inaddition,sensorydysfunctioncanstilloccur.Mostofthepacemakerssetinappropriatesensoryparametersratherthanthemechanicalfailureofthepacemakeritself,includingpoorperceptionandexcessiveperception.
(6)Complicationsandtreatmentrelatedtopacingsystem
1)Pacemakersyndrome(PMS)b>SomepatientswhouseVVIpacemakersmayexperiencedizziness,fatigue,decreasedmobility,hypotension,palpitations,chesttightness,etc.Inseverecases,heartfailuremayoccur,whichiscalledpacemakersyndrome.Treatment:IfPMSoccursandisnotdependentonpacing,thepacingfrequencycanbesloweddowntorestoretheheartrhythmasmuchaspossible,andifnecessary,replacewithanatrioventricularsequentialpacemaker.
2)Pacemaker-mediatedtachycardia(PMT)isatachycardiacausedbytheactiveandcontinuousparticipationofadual-chamberpacemaker.WhentheatrialelectrodesensestheretrogradePwave,theAVDisactivatedandtheventricularpulseisdeliveredattheendoftheAVD.Thelatterexcitestheventricleandthenretrogradestotheventricletoformacircularexercisetachycardia.VentricularprematurecontractionandpooratrialpacingarethemostcommoncausesofPMT.ItcanbepreventedbyprogrammingforalongerPVARP,appropriatelyreducingthesensitivityofatrialperception,delayingtheperceptionoftheatrioventricularinterval,orstartingthepacemaker'sautomaticpreventionprogramforPMT.Terminationmethodsincludeplacingamagnetonthepacemaker,extendingPVARP,program-controlledpacingasatrialinsensitivity(DVI,VVI,DOO)ornon-tracking(DDD)orenablingthepacemaker’sautomaticidentificationandterminationofPMTterminationprocedures.
Follow-upandcommontroubleshooting
Differentfromothercardiacinterventionaltreatments,successfulcardiacpacemakerimplantationisonlythefirststepfordoctorstocompletearelativelysimpletask,whichistediousbutimportantThejobistofollowuppatientsaftersurgeryforalongtime.Thefollow-upworkstartsonthedayofimplantationandrunsthroughthelifeofthepatient.
1.Teachpatientstoself-checktheirpulseaftersurgery
Becausecheckingthepulseisasimpleandeffectivewaytomonitortheworkingconditionofthepacemaker.Whenmonitoringthepulse,makesurethatyouareinthesamephysicalstateeveryday,suchaswhenyouwakeupinthemorningorafter15minutesofsittingstill.
Intheearlystageofpacemakerinstallation,thepacingthresholdisoftenunstableandneedstobeadjustedintime.Therefore,itisnecessarytogotothehospitalforregularcheckups,generallyonceevery2weekswithin1monthaftersurgery,andonceamonthwithin3months(dependingonthepatient'scondition).Therearemanyfactorsthatcausethethresholdtorise.Inadditiontotheelectrodeposition,insufficientsleep,fullmeals,antiarrhythmicdrugs,highbloodpressureandotherfactorsmayhaveanimpact.Therefore,patientsaftersurgeryshouldmaintainagoodmood,ensurearegularlifeandworkandrestsystem,andavoidallpossibleadversefactors.Follow-upcycleandcontentFollow-upshouldbetightatbothendsandlooseinthemiddle.
2.Commonfaultsandtreatment
Usually,thereisnostimulussignal,incapabilitytocapture,orinabilitytoperceive.
(1)Nostimulationpulse
Theremaybeoneofthefollowingcommoncauses:
1)ItcanberesolvedifamagnetisplacedTheproblemismostlyduetoover-sensingortheuseofsomenormalpacingfunctionssuchashysteresis.Theformerismostlycausedbyelectromagneticinterference,myoelectricpotential,cross-sensingorT-waveover-sensing,etc.,sothesensitivityshouldbereduced,whilethelatterdoesnotneedtobedealtwith.
2)Leadorpacemakerfailure:Itmaybeduetolooseordisconnectedscrewsconnectedtothepacemaker,leadconductorfailure,orelectrodeleadinsulationdamageorbatteryexhaustion.Treatment:Tightenthescrewagainorreplacethepacingelectrodeleadorpacemaker.
(2)Failuretocapturemaybeduetooneofthefollowingreasons
1)IncreasedpacingthresholdTheoutputoftheelectrodecannoteffectivelystimulatethemyocardiumconnectedtotheelectrode,whichisanefferentblock.Treatment:Theoutputvoltagecanbetemporarilyincreasedtocorrectthepossiblecauses,suchasapplyinghormones,correctingelectrolytedisturbancesorchangingthepacingposition.
2)Electrodeleadfailure,electrodedislocationorbatteryexhaustionAccordingtospecificreasons,theelectrodeleadshouldbereplacedorrepositionedorthepacemakershouldbereplaced.
(3)Inabilitytoperceive
Itmaybeoneofthefollowingreasons:
1)Theendocardialsignalistoosmall(electrolyteDisorders,temporarychangescausedbyacidosisorpermanentchangesofthelocalendocardiumcausedbymyocardialinfarctionorcardiomyopathy):Atthistime,itisnecessarytoincreasethesensitivityoftheperceptionorchangethepacingposition.
2)Electrodedislocation,malfunction,orpacemakerfailure,accordingtospecificreasons,torepositionorreplacetheelectrodeleadorpacemaker.
Thesafetyofpacemakers
Manypatientsareworriedabouttheinstallationofpacemakers.Infact,itissafetoinstallpacemakers.AlthoughmanypacemakersarelistedaboveHowever,theoverallincidenceisonlyabout1%.Amongpatientswhomeettheindicationsforpacemakerimplantation,ifstandardizedtreatmentandregularfollow-upareavailable,thebenefitsfaroutweighthedisadvantagesforthesepatients.
MoodandHeart
Manypatientsoftenthinkthatthebadmood(emotion)andtheresultingimproperchestareheartdiseaseorcoronaryheartdisease.Actually,themood(Emotionsarenotthesamethingastheheart.Thismisunderstandingisrelatedtothetwowords"heart"inChineselanguage.Infact,themeaningsofthetwoarequitedifferent.Ontheotherhand,itisalsorelatedtotheconceptof"heart"inChinesemedicine.Infact,theconceptof"heart"intraditionalmedicineisevenmoredifferent.It'sclosetomoodandemotions,notall"heart...
ChiefphysicianXuJuntang,PekingUniversityPeople'sHospitalHeartCenterfrom:EncyclopediaFamousMedicalNetwork
