Satelliteclassification
Meteorologicalsatelliteisessentiallyanautomatedhigh-levelweatherstationsuspendedinspace.Itisacombinationofhightechnologysuchasspace,remotesensing,computer,communicationandcontrol.
Duetodifferentorbits,itcanbedividedintotwocategories,namely:sun-synchronouspolarorbitmeteorologicalsatellitesandgeosynchronousmeteorologicalsatellites.Theformeriscalledasun-synchronousorbitmeteorologicalsatellitebecausethesatelliteissynchronizedwiththesunagainstthedirectionoftheearth'srotation;thelatteriscalledageostationaryorbitalmeteorologicalsatelliteandisalsocalledageosynchronousorbitalmeteorologicalsatellite,whichoperatessynchronouslywiththeearthandisnotmovingrelativetotheearth.①Polarorbitingmeteorologicalsatellite.Theflyingaltitudeisabout600-1500kilometers,andthesatellite'sorbitalplanealwaysmaintainsarelativelyfixedangleofintersectionwiththesun.Suchasatellitepassesthroughthesameareatwiceadayatafixedtime,soitcangetaglobalweatherevery12hours.material.②Synchronousmeteorologicalsatellites.Theoperatingaltitudeisabout35,800kilometers,anditsorbitalplanecoincideswiththeearth'sequatorialplane.Seenfromtheearth,thesatelliteisstationaryoveracertainlongitudeoftheequator.Theobservationrangeofasynchronoussatelliteis100longitudespans,from50°southlatitudeto50°northlatitude,and100latitudespans.Therefore,fivesuchsatellitescanformanobservationnetworkcoveringthemiddleandlowlatitudesoftheworld.
Accordingtowhetheritisusedformilitarypurposes,itisdividedintomilitaryweathersatellitesandcivilweathersatellites.
Intheprocessofmeteorologicalforecasting,therearealsotwoformsofshootingsatellitecloudimages:oneisthevisiblelightcloudimagetakenwiththehelpofthereversedegreeofobjectsontheearthtothesun,whichislimitedtoworkduringtheday;Theotheristousethetemperatureofobjectsontheearth'ssurfaceandthedegreeofatmospherictemperatureradiationtoformaninfraredcloudimage,whichcanworkall-weather.
FeaturesofMeteorologicalSatellites
1Orbit(lowandhighorbit).
2Repeatobservationsinashortperiodoftime.
3Thelargeimagingareaisconducivetoobtainingmacro-synchronizationinformationandreducingdataprocessingcapacity.
4Thedatasourceiscontinuousandreal-time,withlowcost.
Orbit:Meteorologicalsatellitesadoptsun-synchronousorbitorgeostationarysatelliteorbit.Inordertoensurethequalityofcloudimages,thesun-synchronousorbitoftheweathersatelliteiscircular,theeccentricityisrequiredtobelessthanonethousandth,theinclinationangleisgreaterthan90°,andthealtitudeisgenerally800to1500kilometers,sothattheimagesobtainedwhenflyingthroughvariousregionsoftheearthhavethesameimageLightconditions.Geostationaryorbitmeteorologicalsatellitesdonothavehighrequirementsforpositionkeepingaccuracy.Theeast-westdirectionisabout0.5°,thenorth-southdirectionisabout1°,andtheeccentricityislessthanonethousandth.
Attitudecontrol:Inordertoensuretheimagequalityofcloudimages,weathersatellitesmusthavehighattitudestability.Meteorologicalsatellitesinsun-synchronousorbitrequireanattitudechangerateoflessthanafewthousandthspersecond,andgeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalsatellitesrequireanattitudechangerateoflessthan0.0002degreespersecondandlessthan0.002degreesperhalfhour.Theattitudecontrolaccuracyofmeteorologicalsatellitesisgenerallyrequiredtobe0.5°~1°.
Datatransmission:Therearefourtypesofweathersatellitedatatransmission:theoriginaldataobtainedbythemeteorologicalremotesensinginstrumentistransmittedtothegrounddataprocessingcenterstation,thecommonfrequencybandis1700MHz,andthedatatransmissionrateisHigh,upto28Mbit/s;thedataobtainedbythemeteorologicalremotesensinginstrumentisinitiallyprocessedonthesatellite,andthemeteorologicaldatasuchascloudpicturesaresenttothegroundinrealtime.Thecommonlyusedfrequencybandsare137MHzand1700MHz,andthedatatransmissionrateislow;Afterthedataobtainedbyremotesensinginstrumentsaretransmittedtothegroundforvariousdataprocessing,themeteorologicaldatasuchascloudpicturesarebroadcastedtovariousplacesthroughmeteorologicalsatellites.Thecommonlyusedfrequencybandis1700MHz;thegroundweatherstations,marineautomaticbuoysandautomaticssetupinunmannedareasarecollected.Thetemperature,pressure,humidityandotherenvironmentaldataobtainedbytheweatherstationarecommonlyusedinfrequencybandsof401and468MHz.
Observationcontents
Themainobservationcontentsofmeteorologicalsatellitesinclude:
①Theshootingofsatellitecloudimages.
②Theobservationofcloudtoptemperature,cloudtopcondition,cloudcoverandphaseofcondensateinthecloud.
③Observationoflandsurfaceconditions,suchasice,snowandsand,andoceansurfaceconditions,suchasoceansurfacetemperature,seaiceandoceancurrents.
④Thetotalamountofwatervaporintheatmosphere,thedistributionofhumidity,theprecipitationareaandthedistributionofprecipitation.
⑤Thecontentanddistributionofozoneintheatmosphere.
⑥Theincidentradiationofthesun,thetotalreflectivityoftheearth-atmospheresystemtosolarradiation,andtheinfraredradiationoftheearth-atmospheresystemtospace.
⑦Themonitoringofspaceenvironmentconditions,suchasthefluxdensityofprotons,alphaparticlesandelectronsemittedbythesun.
Theseobservationshelpusmonitorthemovementandevolutionoftheweathersystem;providealargeamountofbasicdataforthestudyofclimatechange;providealargenumberofenvironmentalmonitoringresultsforspaceflight.
ChinaMeteorologicalSatellite
WindCatchingFamily
ThelatestweathersatelliteFengfeng-1A/Bsatelliteusesthissatellitesignalreflectiontechnologytodetectseasurfacewindspeed.Astheglobalsatellitenavigationsystemmatures,theuseofsatellitenavigationreflectionsignals(GNSS-Rtechnology)toinvertthephysicalcharacteristicsandparametersofthereflectorhasbecomearesearchhotspotinvariouscountries.ChoufengNo.1isaimedatthisdirectionfordevelopmentandconstruction.Whenthesatelliteislaunchedintothesky,theGnss-Rtyphoonobservationradarpayloadstartstowork.Itreceivesthereflectedsignalfromthenavigationsignaltransmittedtotheseasurface,andrealizesthewide-areacarpetsearchanddetectionoftheseasurfacewindfield.Agoodhelperforseasurfacewindfielddetection?Expertsexplainedthatafterthenavigationsignalistransmittedtotheseasurface,specularreflectionoccurs.Thereflectedsignalsformedbycalmwavesandhighwindsandwavesareobviouslydifferent."Whenthereiswind,thereflectedsignalwillchangesectionbysectionwiththewaves.Thegreaterthewind,themoreseverethesignalchange.Byanalyzingthetime-delayDopplerpowerimageandusingtheproportionalrelationshipbetweendifferentparameters,theseasurfacewindspeeddatacanbeinverted."BaiZhaoguangsaidthattheL-bandofnavigationsatelliteshasgoodatmosphericpenetrability,andcanrealizeinformationdetectionofseasurfacewindfieldsthroughouttheday,andcanrealize"precise"forecastsofextremetyphoonweatherthroughmulti-satellitenetworkmonitoring.
FengyunFamily
China’s"FengyunFamily"haslongbeenwell-known.Currently,morethan2500domesticusersandasmanyas70countriesandregionsreceiveanduseFengyunsatellitedata.TheFengyunseriessatelliteshavebeenincludedintheInternationalMeteorologicalServiceSatelliteSequencebytheWorldMeteorologicalOrganization,andarethemainforceofmeteorologicalforecastsintheEasternHemisphere.
In1969,thenPremierZhouEnlaiinstructed:"Wemustbuildourownweathersatellite."Afterdecadesofdevelopment,Chinasuccessfullylaunched4Fengyun-1,7Fengyun-2,and3Fengyun.Threesatellites,thesinglenumberoftheFengyunseriesisapolarorbitingmeteorologicalsatellite,andthedoublenumberisageostationaryorbitingmeteorologicalsatellite.Atpresent,theFengyun-3satellitehascompletelyreplacedtheFengyun-1satellite,andtheFengyun-2isalsobeingreplacedbytheFengyun-4.Fengyun4isChina’ssecond-generationgeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalsatellite,whichisbetterthanFengyun2intermsoftimeresolution,spatialresolution,detectionspectrumanddetectionelements.
Fengyun-1
Chinalauncheditsfirstmeteorologicalsatellite,the"Fengyun-1"sun-synchronousorbitweathersatelliteonSeptember7,1988.TheclarityofthesatellitecloudimageiscomparabletothatoftheUS"NOAA"satellitecloudimage,butitonlyworkedfor39daysduetoamalfunctionofthecomponentsonthesatellite.Aftersuccessfullylaunchingfourpolar-orbitingmeteorologicalsatellites(Fengyun)andthreegeostationarymeteorologicalsatellites(Fengyun-2),ithasexperiencedthedevelopmentprocessfrompolar-orbitingsatellitestogeostationarysatellites,fromexperimentalsatellitestooperationalsatellites.
Atthesametime,ithasalsoestablishedasatellitegroundreceivingandapplicationsystemthatmainlyreceivesFengyunsatellitesandalsoreceivesforeignenvironmentalsatellites,whichhasplayedasignificantroleinmeteorologicaldisastermitigationanddisasterprevention,nationaleconomyandnationaldefenseconstruction.
Currently,mycountry’spolar-orbitingmeteorologicalsatellitesandgeostationarymeteorologicalsatelliteshaveenteredcommercialization.ThesatellitesinorbitareFengyun-1D(launchedin2002)andFengyun-2C(2004).emission).mycountryisoneofthefewcountriesintheworldthathasbothpolar-orbitingandgeostationarymeteorologicalsatellites,andanimportantmemberoftheWorldMeteorologicalOrganization'sEarthObservationSatelliteOperationalMonitoringNetwork.
Fengyun-2
Fengyun-2seriesofgeostationarymeteorologicalsatellitesaremycountry’sfirst-generationgeostationarymeteorologicalsatellites.Sevenofthemareplannedtobelaunched,namelyFengyun-2A/B/C/D/E/F/G,twoteststars(FengyunNo.2A/B),andsixbusinessstars(FengyunNo.2C/D/E/F/G/H).
Fengyun-2,whichhasbeeninservicesince1997,canconductglobalobservationsevery15minutesandregionalobservationsevery6minutes,providingreal-timedynamicdataforclimatemonitoringandweatherforecastinginChinaandtheworld,andtheforecastisaccurateTheratecanreach90%.
Fengyun-3
ThetechnicalindicatorsoftheFengyun-3polar-orbitingmeteorologicalsatellitehavereachedthelevelofthelatestgenerationofmeteorologicalsatellitesinEuropeandtheUnitedStates.Detectedfull-spectrumwide-spectrumdetection,increasedfromkilometer-levelobservationtohundred-meter-levelobservation,receivedfromdomesticnetworkingtoglobalnetworking.
TheFengyun-3E-satellitewassuccessfullylaunchedonJuly5,2021,andbeganitsin-orbittestonJuly23.Itisscheduledtobedeliveredbytheendof2021.Currently,theE-satelliteandtheFengyun-3CandD-satellitesinorbitarenetworkedandoperated,makingChinatheonlycountryintheworldthathastheabilitytonetworkandobservethreeorbitalmeteorologicalsatellitesinthemorning,afternoon,andtwilightatthesametime.
Fengyun-4
At0:11onDecember11,2016,ChinasuccessfullylaunchedtheFengyun-4satellitewiththeLongMarch-3BcarrierrocketattheXichangSatelliteLaunchCenter.
TheFengyun-4satelliteisthefirstsatelliteofmycountry'sgeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalsatellitefromthefirstgeneration(Fengyun-2)tothesecondgeneration.Itisalsomycountry'sfirstgeosynchronousorbitthree-axisstablequantitativeremotesensingsatellite.ThenewlydevelopedSAST5000platformhasadesignlifeof7years.Thesatellitesuccessfullybrokethroughmorethan20corekeytechnologiessuchashigh-precisionimagepositioningandregistration,micro-vibrationmeasurementandsuppression,whichrepresenttheinternationalfrontier,andloadedwithfouradvancedpayloads.Theoverallperformancehasreachedtheinternationaladvancedlevel.
ThemainuserofFengyun4istheChinaMeteorologicalAdministration.Afterthesatelliteisputintouse,weathermonitoringandforecastingandearlywarning,numericalforecasting,andclimatemonitoringcanbecarriedoutmoreaccurately.Thesatellite-mountedlightningimagercantake500lightningpicturesinonesecond,detectthefrequencyandintensityoflightningwithinthearea,andprovidelightningwarningforthefirsttimeinChina.Fengyun-4canobservethetyphoonareaevery3minutes,whichcanmakeupfortheshortcomingsofinsufficientresolutionofsatellitecloudimagesinorbit.Itwillalsoprovidestrongsupportfordisasterandenvironmentalmonitoring,artificialweathermodification,andspaceweatherresearch.
Foreignweathersatellites
In1958,theartificialsatellitelaunchedbytheUnitedStatesbegantocarrymeteorologicalinstruments.OnApril1,1960,theUnitedStatesfirstlaunchedthefirstartificialtestweathersatellite.Attheendof1990,in30years,116meteorologicalsatelliteswerelaunchedallovertheworld,andaglobalmeteorologicalsatellitenetworkhasbeenformed,eliminating4/5oftheworld’smeteorologicalobservationblankareasandenablingpeopletoaccuratelyobtainContinuous,globallawsofatmosphericmovement,accurateweatherforecasts,greatlyreducingcatastrophiclosses.Accordingtoincompletestatistics,ifthereare3to5daysforecastofnaturaldisasters,thelossesinagriculturecanbereducedby30%to50%,andagriculture,animalhusbandry,andfisheryalonecangainanannualbenefitof170millionU.S.dollars.Forexample,from1982to1983,noneofthe33typhoonsthatlandedinChinawasunderreported.TyphoonNo.8607,whichlandednearShantou,Guangdongin1986,reducedlossesbymorethan1billionyuanduetotimelyandaccurateforecasts.
OnApril1,1960,theUnitedStateslaunchedtheworld’sfirstexperimentalweathersatellite"Tyros"1.Thisexperimentalmeteorologicalsatelliteisan18-sidedcylinder,48cmhighand107cmindiameter.ThesatelliteisequippedwithaTVcamera,aremotecontroltaperecorderandaphotodatatransmissiondevice.Itorbitstheearth1,135timesinanearlycircularorbitataheightof700kilometers,andhastaken22,952cloudandtopographicphotos,withausefulrateof60%.Hasthebesttechnicalperformanceatthetime.From1960to1965,theUnitedStateslaunchedatotalof10"Tyros"weathersatellites,ofwhichonlythelasttwoweresun-synchronousorbitsatellites.OnFebruary3,1966,theUnitedStatesdevelopedandlaunchedthefirstpracticalmeteorologicalsatellite"Isa"1.Itisthesecond-generationsun-synchronousorbitmeteorologicalsatelliteoftheUnitedStateswithanorbitalheightofabout1400kilometersandthesub-satellitepointresolutionofthecloudmap.Therateis4000meters.From1966to1969,9satelliteswerelaunchedandalargeamountofmeteorologicaldatawasobtained.Itslaunchsuccessfullyopenedupanewfieldfortheworld'smeteorologicalsatellitedevelopmentandgreatlyreducedvariouslossesduetometeorologicalreasons.
In1969,theSovietUnionfirstlaunchedthe"liucheng"typeImeteorologicalsatellite,whichadoptssun-synchronousorbitsandusuallymaintains2to3satellitesrunningonmutuallyperpendicularorbitalplanes.Inthisway,globalmeteorologicaldatacanbeprovided.Laterthistypeofsatellitewasreplacedbythe"Meteor"2satelliteseries.The"Meteor"Type2satelliteseriesisaseriesofsatelliteswithglobalcoverage.
Japanlaunchedtwogeostationaryweathersatellites,Europe;theSpaceAgencylaunchedtwogeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalservicesatellites,andIndiaalsolaunchedcommunicationsbroadcastingandmeteorologicalmulti-purposesatellites.
OnSeptember7,1988,Chinalauncheditsfirstmeteorologicalsatellite,the"Fengyun-1"sun-synchronousorbitweathersatellite.TheclarityofthesatellitecloudimageiscomparabletothatoftheUS"NOAA"satellitecloudimage,butitonlyworkedfor39daysduetoamalfunctionofthecomponentsonthesatellite.Aftersuccessfullylaunchingfourpolar-orbitingmeteorologicalsatellites(Fengyun)andthreegeostationarymeteorologicalsatellites(Fengyun-2),ithasexperiencedthedevelopmentprocessfrompolar-orbitingsatellitestogeostationarysatellites,fromexperimentalsatellitestooperationalsatellites.
China’spolarorbitingmeteorologicalsatellitesandgeostationarymeteorologicalsatelliteshaveenteredcommercialization.ThesatellitesinorbitareFengyun-1D(launchedin2002)andFengyun-2C(launchedin2004)..Chinaisoneofthefewcountriesintheworldthathasbothpolar-orbitingandgeostationarymeteorologicalsatellites,andanimportantmemberoftheWorldMeteorologicalOrganization'sEarthObservationSatelliteOperationalMonitoringNetwork.
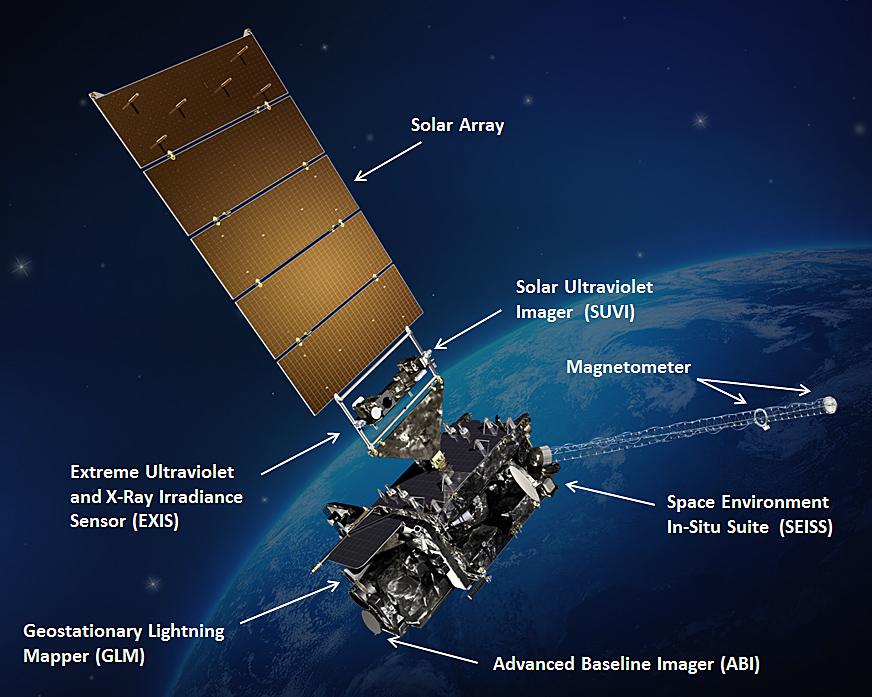
AweathersatellitewiththestrongestscientificperformanceinthehistoryoftheUnitedStatesisscheduledtobelaunchedonNovember19,2016.Atthebestpositionof35,800kilometersfromtheearth(about1/10ofthedistancefromtheearthtothemoon),theGeosynchronousOperationalEnvironmentalSatellite-Rseries(GOES-R)willtakeimagesoftheweatherandatmosphericphenomenasweepingtheUnitedStates.GOES-Rcantakeanimageevery30seconds,whichismuchfasterthanthecurrentGOESmeteorologicalsatellite'sseveralminutesshootinginterval.Thisrapidshootingfunctionenablestheweathersatellitetotrackthedevelopmentandchangesofthunderstorms,hurricanesandotherviolentstorms.
GlobalAtmosphericResearchProject
Thedevelopmentofmeteorologicalsatelliteshasgonethroughtwophasesofexperimentationandapplication.InadditiontotheUnitedStatesandtheSovietUnion,JapanandtheEuropeanSpaceAgencyalsosuccessivelylaunchedmeteorologicalsatellitesin1977.ThesecountriesandorganizationshaveparticipatedinthefirstglobaltestoftheGlobalAtmosphericResearchProgramarrangedbytheWorldMeteorologicalOrganization(WMO).Themainmeteorologicalsatelliteseriesare:
①"Meteor"meteorologicalsatelliteseries:see"Meteor"satellite.
②"Tyros"meteorologicalsatelliteseries:Theworld'sfirstexperimentalmeteorologicalsatelliteserieslaunchedbytheUnitedStates.Atotalof10satelliteswerelaunchedfrom1960to1965.Exceptforthelasttwoinsun-synchronousorbits,therestTheorbitalinclinationanglesare48°and58°.
③"Isa"satellite:ThefirstgenerationoftheUSsun-synchronousorbitmeteorologicalserviceapplicationsatellite.From1966to1969,9satelliteswerelaunchedwithanorbitalinclinationofabout102°andanorbitalheightofabout1,400kilometers.Thesub-satellitepointresolutionofthecloudimageis4kilometers.
④"TyrosN/Noah"satelliteseries:see"TyrosN/Noah"satellite.
⑤"GeostationaryMeteorologicalSatellite"(GMS):Japan’sgeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalserviceapplicationsatellite,atotalof2satellites,launchedin1977and1981respectively,thesub-satellitepointresolutionofvisiblelightandinfraredcloudimagesItis1.25kilometersand5kilometersrespectively.
⑥"Meteosat"(Meteosat):TheEuropeanSpaceAgency'sgeostationaryorbitmeteorologicalservicesatellite,atotalof2satellites,launchedin1977and1981,visiblelight,infraredcloudmapandwatervapormapunderthestarsThepointresolutionis2.5km,5kmand5kmrespectively.
⑦"GeostationaryEnvironmentServiceSatellite":See"GeostationaryEnvironmentServiceSatellite".
⑧"IndianSatellite"(INSAT:India’smulti-purposesatelliteforcommunications,broadcastingandmeteorology.Itsvisiblelightandinfraredcloudimageshavesub-satellitepointresolutionsof2.7kilometersand11kilometers,respectively.
