defined
message authentication means for authentication by signature encryption or transform the message or information related to the message, and the purpose is to prevent the transmission of the stored message is tampered with intentionally or unintentionally, message content including authentication (i.e., authentication message integrity), the source and sink authentication message (i.e., 0 authentication), and serial number, and operation time of the authentication message. It has important applications (such as the Golden Tax system and the bank's tax payment scrambler) in anti-counterfeiting bill.
digest algorithmmessage used for authentication of the general symmetric or asymmetric encryption algorithms, it does not prevent the information from being stolen, but is used to demonstrate the accuracy and integrity of the original, that is, message authentication information is mainly used to prevent tampering.
Message Authentication
message content authentication
content of the message authentication commonly used methods: a message sender to one authentication code (MAC, MDC, etc.) in the message and sending the encrypted to the recipient (sometimes simply encrypted authentication code to). The recipient using the agreed algorithm decrypted message authentication calculation, the resultant authentication code is compared with the received authentication code, if they are equal, the receiver, or rejected. Model
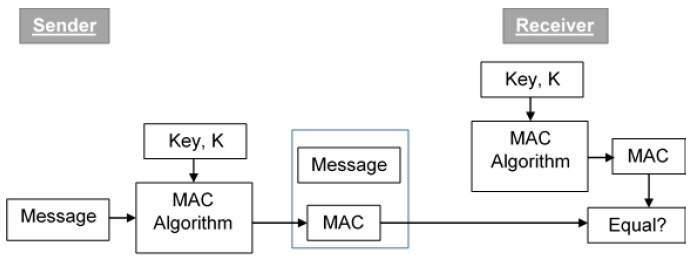
message authentication system
General Modelmessage authentication system 1 shown in FIG. With respect to cryptography, authentication system is more emphasis on integrity. After the message is sent by the sender, the authentication encoder via a control key or no key conversion control, authentication code added to the message transmission channels unperturbed disclosed along with authentication code, the control will also be required to have secret key key transmitted via a secure channel to the receiver. Receiver after receiving all the data, authentication key via the key control or the control without the authentication decoder, it is determined whether the message is complete. Messages are transmitted in clear text or some modification in the way the whole process, but not necessarily require encryption, nor do the contents of the third party confidential. An attacker can intercept and analyze message content transmitted channels and possibly forged messages sent to the recipient fraud. An attacker no longer confidential system cryptanalyst as always in a passive position, but active attacker.
authentication and authentication code decoder shown in FIG. 1can be abstracted as the authentication method of FIG. A secure message authentication system, you must select the appropriate authentication function, which generates an identification mark, and then establish a reasonable authentication protocol based on this, the message recipient to complete the certification.
source and sink authentication
in the authentication message, there are two common message source and sink authentication method.
One is communicating parties agreed in advance to send the message encryption key data, the receiver only needs to confirm whether the message can be transmitted to the plaintext key which can identify the sender. If both sides use the same data encryption key, by embedding it to the sender identifier in the message. Another
is the password communication parties agreed to implement each transmission of the message to send a message containing this password and encryption, the receiver simply determines the password to decrypt the message is equal to the agreed The password will be able to identify the sender. For security reasons, the password should be variable.
message authentication operation time and the number
number and timing of the authentication message is mainly to prevent message replay attacks. Commonly used methods of assembly-line message, the link authenticator and the authentication random tree timestamp.
Message Authentication common attacks and countermeasures
① replay attack: interception of information transmitted when the previously executed agreement, and then used again at some point. A measure against such attacks is in the authentication message containing a distinct value, such as a serial number, a timestamp, a random number or identity of the target identifier embedded like.
② posing attacks: an attacker to impersonate legitimate users to publish false news. To avoid this kind of attack can be used authentication technology.
③ recombinant attack: the one or more previous information when the transmission protocol execution recombined attack. To prevent such attacks, all messaging protocols running all together.
④ tampering attacks: modify, delete, add or replace real news. To avoid this attack can be a message authentication code MAC or a hash function techniques.
