Introduction
SincetheGermanpsychologistHermannEbbinghaus(1850—1909)publishedhisexperimentalreport,memoryhasbecomeoneofthemostexperimentallystudiedfieldsinpsychology.one.Sincethen,memorytheoryandresearchmethodshavecontinuedtodevelop.Theinformationprocessingtheory(orinformationprocessingtheory)thatemergedinthe1950sregardedmemoryasaprocessofencoding,storing,andextractinginputinformation.Accordingtothestoragetime,itisdividedinto:instantaneousmemory,short-termmemoryandlong-termmemory.Althoughthespecificmethods,materials,instruments,andexperimentalconditionsusedbytheresearchersduringthisperiodweredifferent,oneimportantthingincommonamongthesestudiesisthattheyregardmemoryaspeople'sconsciousandexplicitrecoveryofpreviousexperiences.
Memory
Whatismemory
Memoryisthereflectionofpastexperienceinthemind.Allthingsthathavebeenperceivedinthepast,theproblemsthathavebeenthoughtabout,theemotionsthathavebeenexperienced,andtheactionsthathavebeenmanipulatedcanbestoredinthebrainintheformofreflections.Undercertainconditions,suchreflectionscanbeextractedfromthebrain.,Thisprocessismemory.
Memorycanlinkpeople’spastandpresentmentalactivities.Therefore,peoplecancontinuouslyaccumulateknowledgeandexperience,andunderstandthenatureofthingsandtheinnerrelationshipsbetweenthingsthroughthinkingactivitiessuchasclassificationandcomparison.Connection;peoplealsoaccumulatevariousinfluencesonthemselvesthroughmemory,andgraduallyformtheirownpersonality.Therefore,itcanbesaidthatmemoryisthesourceofhumanwisdomandthecornerstoneofhumanpsychologicaldevelopment.
Typesofmemory
Accordingtoitscontent,memorycanbedividedintoimagememory(memoryoftheimageofthingsthathavebeenperceived),episodicmemory(memoryofpersonallyexperiencedevents),Emotionalmemory(memoryoftheemotionsandemotionsyouhaveexperienced),semanticmemory(alsocalledwords-logicalmemory,thatis,thememoryofvariousorganizedknowledgesummarizedbywords),actionmemory(thestateofmovementandactionsofthebody)Skillmemory).
Memoryprocess
Memorystartswithmemorization.Memorizationistheprocessoflearningandacquiringknowledgeandexperience;theprocessofstoringandconsolidatingknowledgeandexperienceinthebrainiscalledretention;theprocessofextractingknowledgeandexperiencefromthebrainiscalledrecall;memorizedmaterialcannotberecalled,butitcanbereproduced.Thereisasenseoffamiliarityandtheabilitytoconfirmthatitisthematerialyouhavetouched.Thisprocessiscalledrecognition.Remembranceisthebeginningofmemoryandthepremiseofretentionandrecall;retentionistheintermediatelinkbetweenremembranceandremembrance;remembranceistheresultofremembranceandretention,andpassingrecollectionisalsoatestofremembranceandretention,andishelpfulConsolidatetheknowledgelearned.
Thephenomenonthatthematerialthathasbeenmemorizedcanneitherberecallednorrecognizediscalledforgetting.In1885,theGermanpsychologistEbbinghausconductedalargenumberofexperimentalstudiesonlearningandmemory,andwasthefounderofexperimentalresearchonmemory.Heusedhimselfasthesubjectandsubject,andusedmeaninglesssyllablesasmemorymaterialstoprovethattheprocessofforgettingisfastandthenslow.Latergenerationsusedhisexperimentaldatatodrawanegativeaccelerationcurvebetweentheholdingamountandtheintervaltime,whichisthefamousholdingcurve.
Representation
Whatisrepresentation
Representationistheprocessofreappearinginthemindoftheimageofthingsthathavebeenperceivedinthepast.Theimageofthingsthatappearinthemindiscalledappearance.
Theroleofrepresentation
Therepresentationisnotonlyintuitiveandvivid,butalsohasacertaingenerality.Representationisaformforpeopletoaccumulateperceptualknowledge.Forawell-informedperson,thecontentofhisrepresentation,thatis,hisperceptualknowledgewillbeveryrich.Representationistheintermediatelinkinthetransitionfromperceptiontothinking,becausetheintuitionoftherepresentationislikeperception;thegeneralityoftherepresentationislikethinking.Althoughthegeneralityofappearanceislowerthanthatofthinking,ithasgeneralityafterall.Thischaracteristicofrepresentationmakesitabridgefromperceptiontothinking.Representationisalsotheperceptualsupportofthinking,whichprovidesmaterialforthinkinginimages,thatis,forimagination.
Threememorysystems
Whatarethreememorysystems
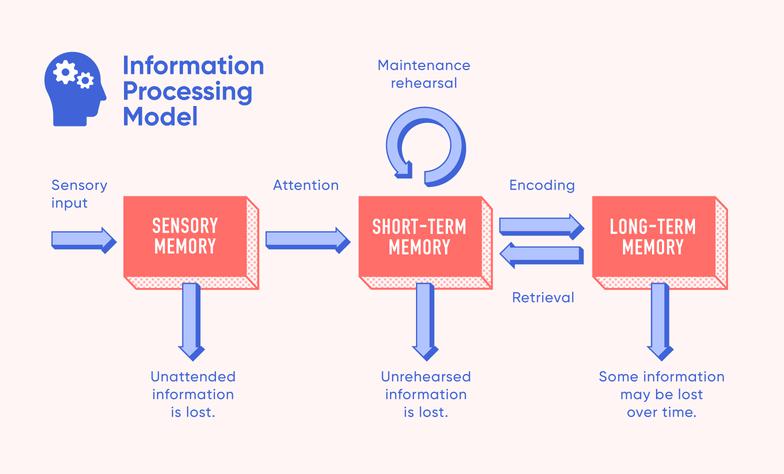
CognitivepsychologyregardsmemoryasthehumanbrainencodingandstoringtheinputinformationAndtheextractionprocess,andaccordingtothedifferentencoding,storageandextractionmethodsofinformation,andthedifferenceinthelengthofinformationstorage,thememoryisdividedintothreesystems:instantaneousmemory,short-termmemoryandlong-termmemory.
Instantaneousmemory
Whatisinstantaneousmemory
Transientmemoryisalsocalledsensorymemoryorsensoryregistration,whichreferstoexternalstimulipresentedinaveryshorttime.Informationisquicklyregisteredinthesensorychannelandretainsamomentofmemory.Ingeneral,thevisualinstantaneousmemoryiscalledimagememory,andtheauditoryinstantaneousmemoryiscalledsoundimagememory.
Characteristicsofinstantaneousmemory
(1)Instantaneousmemoryistheregistrationofexternalstimuliinthesensorychannelintheformofafterimages,soithasaclearimage.
(2)Spolin’sexperimentwithpartialreportingmethodprovedthatthecapacityofinstantaneousmemoryisverylarge,buttheretentiontimeisveryshort.Itisgenerallybelievedthattheinstantaneousmemorycapacityis9-20bits;theimagememoryretentiontimeis0.25-1second,andthesoundimagememoryretentiontimecanexceed1second,butnotlongerthan4seconds.
(3)Ifyoupayattentiontotheinformationintheinstantaneousmemory,youcantransfertheinformationtotheshort-termmemory,otherwisetheinformationwilldisappear.
Short-termmemory
Whatisshort-termmemory
Short-termmemoryreferstoexternalstimulipresentedinaveryshortperiodoftime,andtheretentiontimeis1minuteMemorywithin.
Characteristicsofshort-termmemory
(1)Thecapacityofshort-termmemoryislimited,generally7±2,thatis,5-9items.Ifthecapacityofshort-termmemoryisexceeded,orotheractivitiesareinserted,short-termmemoryiseasilydisturbedandforgettingoccurs.Inordertoexpandthecapacityofshort-termmemory,ablockmethodcanbeused,thatis,combiningsmallmemoryunitsintolargerunits.IfasingleChinesecharacter(people)isturnedintoatwo-characterword(people)toremember,thememorycapacitywillbedoubled.
(2)Languagematerialsaremostlyauditorycodesinshort-termmemory,thatis,itiseasytorememberthesoundsofthelanguage,nottheirimages.
(3)Theinformationintheshort-termmemoryistheinformationcurrentlybeingprocessed,soitcanberealized.
(4)Theinformationinshort-termmemorycanbetransferredtothelong-termmemorysystemafterretelling(mechanicalretellingorfineretellingusingmnemonics).
Long-termmemory
Whatislong-termmemory
Long-termmemorymeansthatexternalstimuliarepresentedinaveryshorttimeandtheretentiontimeismorethan1minuteMemory.
Characteristicsoflong-termmemory
(1)Thecapacityoflong-termmemoryisunlimitedregardlessofthetypeorquantityofinformation.
(2)Thecodingoflong-termmemoryhastwotypes:semanticcodingandimagecoding.Semanticcodingisacodingthatuseswordstoprocessinformationandorganizesitaccordingtothemeaningofthematerial.Imagecodingisthecodingofthemeaningofthingsintheformofsensorymapping.
(3)Iftheinformationstoredinlong-termmemoryisnotrecalledintentionally,peoplewouldnotbeawareofit.Onlywhenpeopleneedtouseexistingknowledgeandexperience,theinformationstoredinlong-termmemorycanbeextractedintoshort-termmemorybeforetheycanberealized.
(4)Theforgettingoflong-termmemoryiscausedbynaturaldeclineorinterference.Interferenceisdividedintotwokindsofproactivesuppressionandbackwardsuppression.Proactiveinhibitionreferstotheinterferenceeffectofpreviouslylearnedmaterialsonmemorizationandrecalloflaterlearningmaterials;invertedinhibitionreferstotheinterferenceeffectoflaterlearningmaterialsonmemorizationandrecallofpreviouslearningmaterials.
Researchprogress
Inrecentyears,somescholarshavechallengedtraditionalmemorytheory.Moreandmoreresearchershaveproposedthatmemoryshouldnotberegardedasasingleentity,butascomposedofdifferentstructures,systemsortypes,whichhavedifferentfunctions.Theycameupwiththetermmultiplememorystructure.Themultiplestructureofmemorymeansdifferenttypesorcombinationsofmemory,anditreferstodifferentmemoryeffectscausedbyprocessesthatareindependentofeachother.Inthepasttenyears,moreandmoreevidencehasrevealedthatthereisarelativelyindependentmemorysystembesidesconsciousexplicitmemory,thatis,implicitmemory.Thecharacteristicofthiskindofmemoryisthatpeopledonotconsciouslyknowthattheyhavethiskindofmemory,itisonlymanifestedintheoperationofaspecifictask.
Theresearchonimplicitmemoryhasbecomethecentraltopicofcognitivepsychologytoday.Theendofthetwentiethcenturywasaperiodofintenseburstofresearchonimplicitmemoryinmemorytheory.Inthisgoldenageofresearch,theresearchonimplicitmemoryhasmadebreakthroughprogress,andresearchinthisareahasbeenincreasing.Forexample,the"JournalofExperimentalPsychology:Learning,Memory,andCognition"fromthe1stto6thissueof1997involvedhalfofthepapersonimplicitmemoryresearch,andthe"PsychologicalResearch"magazineevencomparedthethirdissueof1995withtheThe4thissueoftheboundeditioniscreatedasanimplicitmemoryalbum.
Implicitmemoryreferstotheexperiencethatpeoplecannotrecallthemselvesbutcanproveitsafterthoughtinbehavior(Roediger,1993).Theoperationaldefinitionistheunconsciousextractionofpreviouslyacquiredinformationinteststhatdonotrequireconsciousorexplicitrecallofspecificpastexperiences(grafandschacter,1985).Ebbinghaushasmadeoutstandingcontributionstothestudyofmemory,andthe"forgettingcurve"iswidelyknown.Heoncedividedmemoryintothreecategories,thethirdcategoryisimplicitmemory.Thistypeofmemory"willbereflectedincurrentthoughtsandbehaviors,buttracesofunconsciousparticipationinthisprocess."Healsopointedoutthatthistypeofmemorycannotbedetectedby"introspection."Becauseofthelimitationofdetectionmethods,theresearchonimplicitmemorywasinterruptedinthelongyearsafterEbbinghaus.Itwasnotuntilthe1960sand1970sthatimplicitmemorysurfacedagainduetoamnesiaresearchandbecameoneoftheresearchhotspots.
Theprogressofscientificresearchlargelydependsontheinnovationofresearchmethods.Sofar,theresearchmethodsofimplicitmemoryhavegonethroughthreemainstages.Before1991,thetaskseparationparadigmwasmainlyadopted;in1991,theseparationprocedurewasadoptedtostudyimplicitmemory;recently,theresearchofimplicitmemorybegantoenterthemodelingstage.
References
"CognitivePsychology"(English)Eysenck
"CognitivePsychology"(U.S.)JohnB.Best
p>"CognitivePsychology"(WangSu)
"CognitivePsychology"(PengDanling)
"ContemporaryCognitivePsychology"LiangNingjian
"MemoryPsychology"YangZhiliang
