Drug development is an intricate process that spans from the conceptual stage of a new compound to its eventual market launch. At the heart of this process is the assessment of how a potential new drug interacts with the human body, and one pivotal method of making this determination is through "in vivo ADME testing".
Exploring the Basics of In Vivo ADME Testing
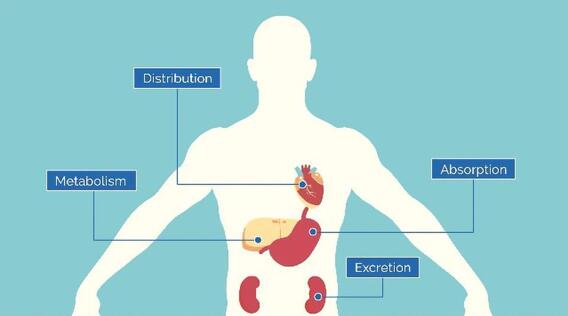
ADME is an acronym that stands for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion. In simpler terms, ADME evaluates:
Absorption: How is the drug taken up by the body?
Distribution: How does the drug move around and where does it end up within the body?
Metabolism: How does the body transform the drug?
Excretion: How does the body eliminate the drug?
"In vivo" means that these tests are carried out on living organisms, typically laboratory animals. In contrast, "in vitro" testing is done outside of a living organism, often in a test tube or petri dish.
The Critical Need for In Vivo ADME Testing
In the world of drug development, it's not just about finding compounds that can target a specific illness or ailment. It's equally crucial to understand the journey of these compounds within the human system. Without this insight, a potential drug could have unintended effects or not work as intended. Moreover, the results from in vivo ADME tests can influence dosage recommendations, highlight potential drug interactions and identify any potential toxic metabolites. Ultimately, these findings ensure the safety and efficacy of a new drug before it reaches human trials.
In Vivo ADME Testing: Tools and Techniques
Selection of Test Subjects: Typically, rodents like rats and mice are first-line subjects due to their well-understood biology and similarities to human systems. Depending on the drug and the target ailment, other animals might also be considered.
Administration: The drug is administered, often orally, to see how it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Depending on the nature of the drug, other methods like intravenous injections might be used.
Sampling: Various samples such as blood, urine, and feces are collected at specific intervals to analyze the concentration of the drug and its metabolites.
Analysis: Advanced analytical techniques, such as liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, are employed to measure the presence and concentration of the drug and its metabolites in the samples.
Data Interpretation: The gathered data provides insights into the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of the drug. PK deals with what the body does to the drug (metabolism rate, distribution, etc.), while PD investigates what the drug does to the body (therapeutic effects, potential side effects).
Innovations in In Vivo ADME Testing
Recent advances in technology and methodologies have enhanced the precision and relevance of in vivo ADME tests. Techniques such as microdosing, where sub-therapeutic amounts of the drug are used, have become more popular. This allows researchers to glean ADME information with reduced risk to the test subjects. Furthermore, the rise of computational methods and artificial intelligence is revolutionizing predictions related to drug metabolism and interactions, making the drug development process more efficient and accurate.

Conclusion
in vivo adme testing is an indispensable part of the drug development pipeline. By understanding how potential drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted, researchers and pharmaceutical companies can ensure that they are not only effective but safe for human consumption. With continued advancements in technology and methodologies, the future of in vivo ADME testing promises even more accuracy and efficiency, paving the way for safer and more effective drugs for the global population.
