principle
Gas molecules are doing unregistered thermal movements.
Diffusion is a substance migration resulting from the thermal movement of particles (molecules, atomic, etc.). It can be carried out by one or more substances within the same phase of gas, liquid or solid phase, mainly due to poor concentration, and the temperature difference and turbulence movement.
The fine particles migrate from a large region to a smaller region until the concentration of each portion in one phase reaches a consistent or two-phase concentration to a balance.
Diffusion speed is the largest in the gas, the liquid is secondary, the solid is the smallest. The concentration is too large, the smaller particles are small, the higher the temperature, the faster diffusion.
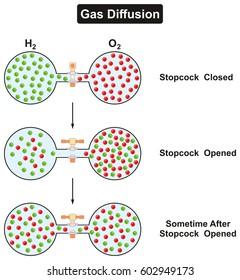
Gas diffusion law
One method of separating gas mixture. According to the gas molecular motion, the gas mixture is fast, the light molecule is fast, and the higenous wall is more, the movement speed of the hemonium is slow, and the opportunity of the impactor wall is small. If the wall has a numerous microporous, each hole is allowed to pass by the molecule alone, and the chance of the light molecule passes must be more than the weight.
The diffusion result is that light molecules in the device are relatively reduced, enriched in the outside of the device; the henoconics in the device increases relatively, and is enriched in the device. Therefore, some degree of separation can be obtained. This method is mainly used for separating isotope. A mixed gas having a small molecular weight, such as the hexafluoride of uranium 235 and uranium 238, must be continuously performed to achieve the desired degree of separation.
Calculation method
Diffusion Rate Calculation
The diffusion rate is measured by the precision balance weighing diffusion tube at a certain amount of time interval, And calculate it in the formula.
Type DR - diffusion rate, μg / min;
M-diffusion weight loss, g;
t - weighing Time lapse, min.
If the diffusion rate DR (measured value) and the flow rate of the dilution, the components content of the standard gas can be calculated in the formula.
C - standard gas content, μg / l
DR - diffusion ratio, μg / min;
F - dilute gas flow, Ml / min;
k - constant determined by the species of the gas, K = 22.4W × (273 + T) × 1273 × P / 760;
W-- The relative molecular mass of the component gas;
T - temperature, ° C
P - atmospheric pressure, mmHg.
Related Theory
Molecular Theory
People from the micro-model of molecular sports, give some simplified assumption, combined probability, and statistical knowledge It is proposed that gas molecular motion theory, which is mainly composed of
(1) gas consisting of molecules, the molecule is a small particle, and the distance between each other is much larger than the diameter of the molecule, molecular volume and The gas volume can be omitted.
(2) Gas molecules are in a certain speed in each direction in each direction at different speeds. A typical example is a diffusion phenomenon, Brown movement.
(3) In addition to colliding with each other, the interaction between gas molecules is very weak, or even negligible.
(4) Gas molecules collide with each other or the collision of the wall is elastic collision.
(5) The average kinetic energy of the molecule is proportional to the thermodynamic temperature.
(7) There is a interaction force between molecules. At the same time, there is an increase in gravity and repulsiveness, gravitational and repulsive force, which increases with the distance between the molecular distances, but the change induced is fast than the gravity, and the actual performance is the synerg of gravity and repulsiveness.
