FAT table class
FAT file system has FAT12, FAT16, FAT32. The three types of the above are classified by the length of each FAT entry in the FAT table, that is, each of the FAT tables in FAT12 occupies 12 bits, FAT16's FAT table Each FAT entry takes up a 16-bit, and each FAT table item in the FAT table of FAT32 takes up 32 bits.
FAT table location
FAT file system The space of the logical disk is roughly divided into three parts, and the DBR and the reserved sector (FAT1, FAT2), data District (DATA).
DBR only accounts for one sector, then there are 31 reserved sectors. After the file allocation table is followed by DBR and retained sectors, FAT1's specific address offset is 0EH ~ 0FH, FAT2 follows FAT1, and its address can be added to the sector number of FAT1 plus each FAT. The number of sectors accounted for. (It should be noted that the FAT16 file system only DBR, accounting for one sector, no reserved sector.)
FAT table is created by the formatting program in formatting the partition, the specific number is guided The offset of the sector is 0x10 byte FAT1 is active FAT, FAT2 is backup FAT [1]. The FAT file system generally has two FAT tables because the storage space (cluster chain) and free space management of the file is implemented by FAT, and FAT is so important, saving two to the first corruption, there is also the first Two available, but for some smaller storage media allows only one FAT table.
FAT table consists of
FAT table consists of a FAT entry. Each FAT entry has a size of 12, 16 bits, and 32 digits. Each FAT entry has a fixed number, this number starts from 0.
FAT table 0 and 1 of the FAT table items have specialized purposes. The 0th FAT entry is usually used to store the media type where the partition is located; the FAT entry is used to store the dirty flag of the file system, indicating that the file system is illegally uninstalled or an error in the disk surface.
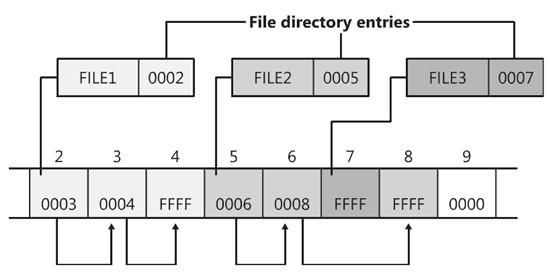
Each FAT entry maps a cluster of the FAT data area. Because the No. 0 FAT entry and the first FAT entry have special purposes, it cannot form a mapping with clusters in the data area, so starting with the first cluster map in the data area from the 2nd FAT entry, because of this, data The first cluster in the area is numbered 2 clusters, which is also the cause of the cluster and 1 cluster. The 3rd cluster is mapped with the No. 3 FAT entry, and the 4th cluster is mapped with the No. 4 FAT entry to this class until the last cluster in the data area.
FAT table Function
-
indicates the type of media in the partition.
-
indicates the cluster chain allocation of each cluster occupied by a file. Each cluster maps a FAT item in the FAT table, and the FAT item records the cluster chain of the file in a pointer.
-
indicates that bad clusters and available clusters. Bad clusters are in the formatting process, found and record them in the corresponding FAT entry. In a cluster, as long as there is a problem with a sector, the cluster cannot be used. Take FAT16 as an example. If the partition is formatted, the bad sector is found, that is, write FFF7h in the table item of the corresponding cluster, indicating that the sector of the cluster cannot be used, and the system will not assign it to the user file.
FAT table
If a FAT entry is non-zero, it means that this cluster has been allocated. A non-zero FAT entry may be the next cluster number of a file, or it is possible to be a good file end tag, or a bad cluster tag. If you are looking for a file's next cluster, you only need to view the FAT item corresponding to the start cluster number described in the directory item of the file. If the file has only one cluster, the value here is an end tag; if The file is not only a cluster, then the value here is the cluster number of it next cluster.
For the management of the FAT entry, the FAT16 file system is used as an example, and its FAT entry is 16-bit, that is, each FAT item accounts for 2 bytes. The 16-bit FAT table item is managed by 65,535 clusters. In the Windows 2000 system, the cluster size is 64 sectors (32KB), so that the maximum management of the FAT16 operating system can manage 32 * 65535 = 209120kb = 2048MB = 2GB partition. For hard drives that have more than 2GB of capacity, it must be divided into multiple partitions that do not exceed 2GB. From the Windows 2000 system, the cluster size can reach 128 sectors (64KB), and the FAT16 file system can manage 4GB partitions, but this partition is inaccessible before Windows 2000.
