Meaning and forming
Electronic capture reaction belongs to an β decay, and sometimes it is called inverse β decay.
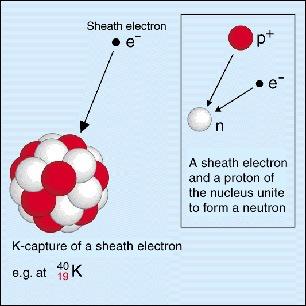
In electronic capture, electrons on an inner track (usually electrons from k electronics or L electronics, called K-capture and L-capture), one of the nucleus proton capture a neutron and forming an electron neutrino. Because a proton becomes a neutron, the neutron number of the nucleus is added 1, the number of protons is 1, and the mass of the atom does not change. Since the reaction reduces the number of protons 1, the electronic capture reaction converts an element into a new element. The newly generated atom is excited, to the basic transition of the beam (a electromagnetic radiation) photon; the principle of the light and the number of light, the reaction also has an electronics in electronics (the first experiment in human history confirmed China] The existence is achieved by observing the observation of the electron capture reaction!); A Russian Effect is sometimes released, and the Auger Electrons is released.
Unique decay
Electronic capture is an atomic nucleus having an atomic number of rectumes but lacks sufficient energy to release positron. If the energy difference of the initial nucleus and the generated new nucleus is less than 1.022 meV, the positive electron emission is banned, and the electronic capture is the only decay method. For example, 铷 -83 will only be used by electron capture fading into a helium-83 because the energy difference of both is only about 0.9 MeV.
relies only by electron capture to decay radioactive elements, in theory, it can be disabled by disabling all electron ions. Therefore, there is a hypothesis that the ultra-new star is completely radiated, so that these radioactive elements have not undergone decay, and in the following time, as long as there is no electronic, it is not in the outer space. There has been no decay. Some abnormal distribution of element abundances may be relevant.
Affecting Factors
The chemical bond affects the electronic capture reaction to a certain extent (usually less than 1% of the degree of imply) by changing the degree of electrons near the nucleus.
In the intermediate portion of the element cycle table, the isotopes whose isotope is generally made of electron capture, and the isotope that is more than stable homologous vesors is usually decreated by β decay. A good example is the radioisotope of the silver element, and its light isotope is decremented by electron capture (inverse β decay), and is the β decrease in isotope.
