Function effect
The disk quota can limit the disk space that the specified account can use, so as to avoid the excessive use of disk space by a user that causes other users to not work properly or even affect the system operation. This function is very important in server management, but it is of little significance to stand-alone users.
In the windows series, only win2000 and later versions and using the NTFS file system can achieve this function.
Set Disk Quota
Take the Windows Server 2003 system as an example to introduce the method of setting disk quota:
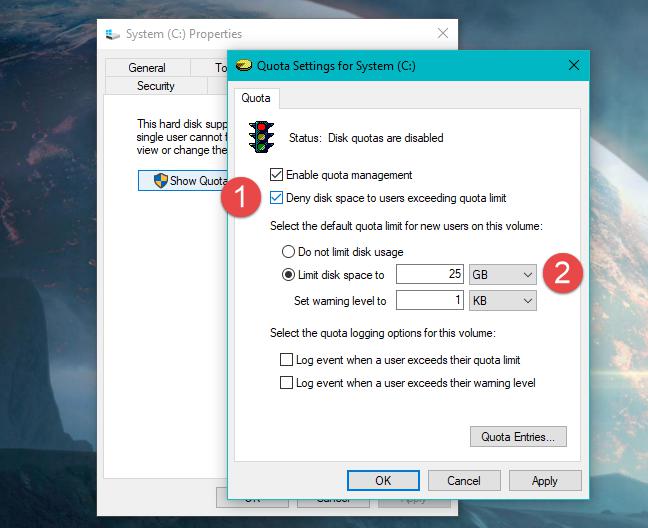
Step 1, in the "My Computer" window Right-click the disk partition where the shared folder is located, and select the "Properties" shortcut command to open the disk properties dialog box. Then switch to the "Quota" tab, and keep the check boxes of "Enable quota management" and "Reject disk space to users exceeding the quota limit" checked. In addition, it is recommended to check the two checkboxes of "Log event when user exceeds quota limit" and "Log event when user exceeds warning level" to record quota alarms in the log. Then click the "Quota Item" button.
Step 2, open the "Quota Item for Local Disk" window, click the "Quota" → "New Quota Item" menu command in turn, find and select the target in the "Select User" dialog box that opens User and click the "OK" button.
Step 3, in the "Add New Quota Item" dialog box that opens, select the "Limit Disk Space to" radio box and set the space size to 100MB. Then set the space size to 95MB in the "Set warning level to" edit box. Finally, click the "OK" button to make the settings take effect.
Step 4, return to the "Local Disk Quota Item" window, repeat the above steps to create a new quota item for other users, close the window after setting, return to the "Local Disk Properties" dialog box and click "OK "Button. The user who sets the quota item can only use the disk space within the specified capacity.
Interpretation example
The disk quota tracking of NTFS volumes and the control of disk space usage. Administrators can configure Windows to:
When the user exceeds the specified disk space limit (that is, the amount of disk space that the user is allowed to use), prevent further use of disk space and log events.
Log an event when the user exceeds the specified disk space warning level (that is, the point at which the user is close to his quota limit).
When starting disk quota, two values can be set: disk quota limit and disk quota warning level. For example, you can set the user's disk quota limit to 500 MB, and set the disk quota warning level to 450 MB. In this case, users can store files up to 500 MB on the volume. If users store more than 450 MB of files on the volume, the disk quota system can be configured to record system events. Only members of the Administrators group can manage quotas on the volume. For instructions on setting disk quota values, see Assign default quota values.
You can specify that users can exceed their quota limits. If you do not want to deny users access to the volume but want to track the disk space usage of each user, enabling quotas and not restricting disk space usage is very useful. You can also specify whether to log events regardless of whether the user exceeds the quota warning level or exceeds the quota limit.
When the volume disk quota is enabled, the system will automatically track the new user volume usage from that value.
As long as the volume is formatted with the NTFS file system, quotas can be activated on local volumes, network volumes, and removable drives. In addition, network volumes must be shared from the root directory of the volume, and removable drives must also be shared. The Windows installation will automatically upgrade volumes formatted with the version of NTFS in Windows NT.
Because compressed files are tracked by their uncompressed size, file compression cannot be used to prevent users from exceeding their quota limits. For example, if a 50 MB file is compressed to 40 MB, Windows will calculate the quota limit based on the initial 50 MB file size.
In contrast, Windows will track the usage of compressed folders and calculate the quota limit based on the compressed size. For example, if a 500 MB folder is 300 MB after compression, Windows will only calculate the quota limit as 300 MB.
