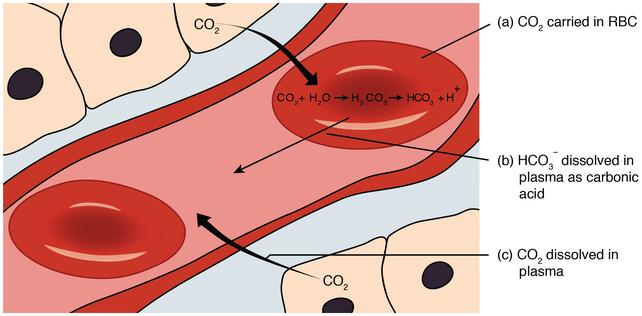
The pH of the solution may be appropriately determined by the change in the concentration ratio of the acid and its salt. When a strong base BOH is added to this solution, HA + B + OH- → H2O + B A- is increasing between the weak acid HA in the solution, and OH- disappears. Further, when the strong acid HA is added, the reaction is reacted with the salt MA, and becomes M + A- + H + A- → Ha + M + A-, at this time h disappears. Such a mixture of weak acids and its salts eliminate the H and OH-ions added. The mixed solution of a weak base and its salt is also the same. The original and plasma of the organism is a buffer having such a nature, and therefore often show the tendency (abbreviated state) that holds a pH. The inorganic acid or salt of a buffer system in the biological body is a carbonate and a hydrogencarbonate (carbonated system) and the phosphite and phosphate (phosphate buffer system), which serves the main role in the blood in the tissue cells. The main role is the main role, but the protein (hemoglobin and plasma protein in the blood) or amino acid is also large. Further, in the biological experiment, a solution for use as an organ or tissue often requires a buffer, and is a variety of phosphate buffers, acetic acid buffer, and the like.