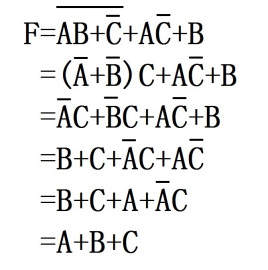DiscoveringHistory
Discovering
Britishmathematiciansproposedin1847and1854inordertostudythelawsofthinking(logic,mathematicallogic)Mathematicalmodel.Sincethen,R.Dai
Dejinregardsitasaspecialstyle.Duetothelackofphysicalbackground,theresearchwasslow,andnewprogresswasmadeinthe1930sand1940s.Around1935,MHStonefirstpointedoutthatthereisaclearconnectionbetweenBooleanalgebraandrings,whichmakesBooleanalgebraintheoryTherehasbeenacertaindevelopment.Booleanalgebrahasapplicationsinalgebra(algebraicstructure),logicalcalculus,settheory,topologicalspacetheory,measurementtheory,probabilitytheory,functionalanalysisandotherbranchesofmathematics;after1967,ithasbeenusedintheaxiomsofoneofthebranchesofmathematicallogicItalsoplaysacertainroleinthetheoreticalresearchofchemicalsettheoryandmodeltheory.Inrecentdecades,Booleanalgebrahashadimportantapplicationsinautomationtechnology,logicdesignofelectroniccomputersandotherengineeringtechnologyfields.
In1835,20-year-oldGeorgeBullopenedaprivateschool.Inordertoprovidestudentswithnecessarymathematicscourses,hereadsometextbooksthatintroducedmathematicswithgreatinterest.Soon,hewassurprised,arethesethingsmathematics?It'sincredible.Therefore,thisyoungmanwhohadonlyreceivedpreliminarymathematicstrainingtaughthimselfthedifficult"CelestialMechanics"andtheveryabstract"AnalyticalMechanics".Becausehehasastrongsenseofthesymmetryandbeautyofalgebraicrelations,inhislonelyresearch,hefirstdiscoveredinvariantsandpublishedthisresultasapaper.Afterthepublicationofthishigh-qualitypaper,Bullstillremainedinelementaryschooltoteach,buthebegantocommunicateorcorrespondwithmanytopBritishmathematicians,includingmathematicianandlogicianDeMorgan.Morganwasinvolvedinafamouscontroversyinthefirsthalfofthe19thcentury.BullknewthatMorganwasright,soin1848hepublishedathinbooklettodefendhisfriend.Thisbookisapreviewofsomethinggreaterforhimin6years.Whenitcameout,itimmediatelyarousedMorgan'spraiseandaffirmedthatheopenedupnewandtrickyresearchsubjects.Booleanwasalreadystudyinglogicalalgebra,namelyBooleanalgebra.Hesimplifiedlogicintoanextremelyeasyandsimplealgebra.Inthiskindofalgebra,the"reasoning"ofappropriatematerialsbecomestheelementarycalculationofformulas,whicharemuchsimplerthanmostformulasusedinthesecondgradeofalgebrainmiddleschoolinthepast.Inthisway,logicitselfissubjecttomathematics.Inordertoperfecthisresearchwork,Bullmadeextraordinaryeffortsforthenext6years.In1854,hepublishedthemasterpiece"TheLawsofThinking",whenhewas39yearsold,Booleanalgebracameout,andsetanewmilestoneinthehistoryofmathematics.Likealmostallnewthings,Booleanalgebrahasnotreceivedmuchattentionafteritsinvention.FamousmathematiciansontheEuropeancontinentcontemptuouslycalleditaphilosophicallyweirdthingwithnomathematicalmeaning.TheysuspectedthatmathematiciansfromtheBritishIslescouldmakeuniquecontributionstomathematics.BulldiedshortlyafterhisJiewaspublished.Atthebeginningofthe20thcentury,Russellbelievedin"PrinciplesofMathematics"that"PuremathematicswasdiscoveredbyBooleaninaworkhecalled"TheLawofThinking"."ThisstatementimmediatelyattractedtheattentionoftheworldtoBooleanalgebra.Today,thelogicalalgebrainventedbyBooleanhasdevelopedintoamajorbranchofpuremathematics.
Indiscretemathematics,Booleanalgebra(sometimescalledBooleanlattice)isasupplementarydistributivelattice(refertothedefinitionoflattice).Youcanthinkofelementsinvariousways;themostcommonistotreatthemasAsageneralizedtruthvalue.Asasimpleexample,supposethatthreeconditionsareindependentlytrueorfalse.TheelementsofBooleanalgebracanthenspecifyexactlythosethataretrue;thenBooleanalgebraitselfwillbeacollectionofalleightpossibilities,andthewaytocombinethemtogether.
ArelatedtopicsometimescalledBooleanalgebraisBooleanlogic,whichcanbedefinedassomethingcommontoallBooleanalgebras.ItconsistsofrelationshipsthatalwaysholdbetweentheelementsofBooleanalgebra,regardlessofwhichBooleanalgebrayouhave.Becausethealgebraoflogicgatesandcertainelectroniccircuitsisalsolikethisinform,Booleanlogicisalsostudiedinengineeringandcomputerscience,justlikeinmathematicallogic.
TheoryofOperations
BasicTheory
TheoperationsonBooleanalgebraarecalledAND(and),OR(or)andNOT(not).IfthealgebraicstructureisBooleanalgebra,theseoperationsmustbehaveliketwo-elementBooleanalgebra(thetwoelementsareTRUE(true)andFALSE(false)).Alsoknownaslogicalalgebra.Boolean(Boole,G.)isamathematicaltoolproposedin1847tostudythelawsofthinking(logic).BooleanalgebrareferstothealgebrasystemB=〈B,+,·,′〉
ItcontainssetBtogetherwithtwobinaryoperations+,·andaunaryoperationdefinedonit.Booleanalgebrahasthefollowingproperties:Foranyelementa,b,cinB,thereare:
1.a+b=b+a,a·b=b·a.
2.a·(b+c)=a·b+a·c,
a+(b·c)=(a+b)·(a+c).
3.a+0=a,a·1=a.
4.a+a′=1,a·a′=0.
BooleanalgebracanalsobeabbreviatedasB=〈B,+,·,′〉.Inthecaseofnotbeingconfused,itwillalsosetBiscalledBooleanalgebra.ThesetBofBooleanalgebraBiscalledBooleanset,alsoknownasthedomainordomainofBooleanalgebra.ItisthewholeoftheobjectsstudiedbyalgebraB.Generally,Booleansetsarerequiredtohaveatleasttwodifferentelements.0And1,anditselementsareclosedtothethreeoperations+,·,′,sonotanysetcanbecomeaBooleanset.Inthecaseofafiniteset,thenumberofelementsinaBooleansetcanonlybe2n,n=0,1,2,…Binaryoperation+iscalledBooleanaddition,Booleansum,Booleanunion,Booleandisjunction,etc.;binaryoperation·calledBooleanmultiplication,Booleanproduct,Booleanintersection,Booleanconjunction,etc.;unaryoperation'iscalledBooleanComplement,Booleannegation,remainderoperationofBooleanalgebra,etc.TherearealsoothernotationsfortheoperationsymbolsofBooleanalgebra,suchas∪,∩,-;∨,∧,?etc.BecauseBooleanalgebrawithonlyoneelementhaslittlepracticalvalue,Itisusuallyassumedthat0≠1,and0iscalledthezeroelementorminimumelementofBooleanalgebra,and1istheunitelementormaximumelementofBooleanalgebra.BooleanalgebraisusuallydefinedbyHuntington'saxiomsystem,butitcanalsobedefinedbyBean'saxiomsystemorhas0Complementaryallocationwith1isdefined.
BooksonBooleanalgebra(2photos)
Example
ThesimplestBooleanalgebrahasonlytwoelements,0and1.Anddefinedbythefollowingrules(truthtable):
∧ | 0 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 1 |
∨ | 0 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 |
¬ | 0 | 1 |
1 | 0 |
Itisusedinlogic,interpreting0asfalseand1Istrue,∧isand,∨isor,¬isnot.ExpressionsinvolvingvariablesandBooleanoperationsrepresenttheformofstatements.Twosuchexpressionscanbeprovedtobeequivalentusingtheaboveaxiomsifandonlyifthecorrespondingstatementformsarelogicallyequivalent.
Two-elementBooleanalgebraisalsousedincircuitdesigninelectronicengineering;here0and1representtwodifferentstatesofabitinadigitalcircuit,typicallyhighandlowvoltage.Circuitsaredescribedbyexpressionscontainingvariables.Twosuchexpressionsareequivalenttoallthevaluesofthesevariablesifandonlyifthecorrespondingcircuithasthesameinput-outputbehavior.Inaddition,allpossibleinput-outputbehaviorscanbemodeledusingappropriateBooleanexpressions.
Two-elementBooleanalgebraisalsoimportantinthegeneraltheoryofBooleanalgebra,becauseequationsinvolvingmultiplevariablesareuniversallytrueinallBooleanalgebras,ifandonlyifitisinthetwo-elementItistrueinBooleanalgebra(thiscanalwaysbeconfirmedbytrivialbruteforcealgorithms).Forexample,toprovethatthefollowinglaw(Consensustheorem)isuniversallyvalidinallBooleanalgebras:
(a∨b)∧(¬a∨c)∧(b∨c)≡(a∨b)∧(¬a∨c)
(a∧b)∨(¬a∧c)∨(b∧c)≡(a∧b)∨(¬a∧c)
Thepowerset(setofsubsets)ofanygivensetSformsaBooleanalgebrawithtwooperations∨:=∪(union)and∧:=∩(intersection).Thesmallestelement0istheemptysetandthelargestelement1isthesetSitself.
ThesetofallsubsetsofafiniteorcofinitesetSisaBooleanalgebra.
Foranynaturalnumbern,thesetofallpositivedivisorsofnformsadistributivelattice,ifwewritea≤bfora|b.ThislatticeisaBooleanalgebraifandonlyifnissquare-free.Thesmallestelement0ofthisBooleanalgebraisthenaturalnumber1;thelargestelement1ofthisBooleanalgebraisthenaturalnumbern.
AnotherexampleofBooleanalgebracomesfromatopologicalspace:IfXisatopologicalspace,whichisbothopenandclosed,thecollectionofallsubsetsofXhastwooperations∨:=∪(Union)and∧:=∩(intersection)Booleanalgebra.
IfRisanarbitraryring,andwedefinethesetofcentralidempotentas
A={e∈R:e2=e,ex=xe,x∈R}
ThensetAbecomesaBooleanalgebrawithtwooperationse∨f:=e+f+efande∧f:=ef.
FeaturesandExamples
TouseBooleanalgebra,youmustunderstandthefeaturesofBooleanalgebra:
Elementsaremembersofaset.Forexample:A1,representedbyA1∈B.IfA1isnotanelementofthisset,itisrepresentedbyA1B.
ThecompletesetisthesetX,whichcontainsalltheelementsinthesetX.
Anemptysetmeansthatthesetdoesnotcontainanyelements.
Asubsetisasetthatcontainssomeelements,suchasA,whichcontainstheelementsA1andA2inthesetX,representedbyA∈B.
Unaryoperationistooperateonasingleset(suchasA),thepurposeistofindtheelementsinthecompletesetexceptforsetA,denotedby¬A.
Thebinaryoperationistooperateontwosets(suchasA1,A2),thepurposeis:tofindthecommonelementsofthetwosets,representedbyA1∧A2;findtwoAllelementsofasetarerepresentedbyA1∨A2.
AfterunderstandingtheabstractcharacteristicsofBooleanalgebra,weuseexamplestointroducehowtouseBooleanalgebratoperformsetoperations.SetsetBcontainselements{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10},subsetA1containselements{1,2,3,4,5},subsetA2Containselements{3,4,5,7,10}.Thenthecorrespondingoperationresultis:
¬B=¬1=0,whichmeansanemptyset.
¬A1={6,7,8,9,10}.
A1∧A2={1,2,3,4,5}∧{3,4,5,7,10}={3,4,5}.
A1∨A2={1,2,3,4,5}∨{3,4,5,7,10}={1,2,3,4,5,7,10}.
OrderTheory
Image:Hassediagramofpowersetof3.png
TheBooleanlatticeofthesubsetisthesameasanylattice,Booleanalgebra(A,,)canleadtoapartiallyorderedset(A,≤),bydefinition
a≤bwhenAndonlyifa=ab(itisalsoequivalenttob=ab).
Infact,youcanalsodefineBooleanalgebraasadistributivelattice(A,≤)withthesmallestelement0andthelargestelement1(consideredasapartiallyorderedset),inwhichallelementsxhavecomplements¬xsatisfies
x¬x=0andx¬x=1
hereandareusedtoindicatetheinfimum(intersection)andsupremum(union)oftwoelements.Also,ifcomplementsintheabovesenseexist,theyareuniquelydeterminable.
Theviewpointsofalgebraandordertheorycanusuallybeusedinterchangeably,andbothareofimportantuse.Resultsandconceptscanbeintroducedfromuniversalalgebraandordertheory.Inmanypracticalexamples,orderrelations,conjunction(logicalAND),disjunction(logicalOR)andnegation(logicalnegation)areallnaturallyavailable,sothisconnectioncanbeuseddirectly.
Principleofduality
YoucanalsoapplythegeneralunderstandingofdualityfromordertheorytoBooleanalgebra.Inparticular,theorderdualityofallBooleanalgebras,orequivalently,thealgebrasobtainedbyswappingandarealsoBooleanalgebras.Generallyspeaking,anyvalidlawofBooleanalgebracanbetransformedintoanothervalidduallawbyswapping0and1,and,and≤and≥.
Othernotation
TheoperatorsofBooleanalgebracanbeexpressedinvariousways.TheyareoftensimplywrittenasAND,OR,andNOT.Whendescribingthecircuit,youcanalsouseNAND(NOTAND),NOR(NOTOR),andXOR(exclusiveOR).Mathematicians,engineers,andprogrammersoftenuse+forORand·forAND(becauseinsomerespectstheseoperationsaresimilartoadditionandmultiplicationinotheralgebraicstructures,andtheseoperationsareeasyforpeoplefamiliarwithordinaryalgebratogettheproduct.Andnormalform),andtoexpressNOTasdrawingahorizontallineontopoftheexpressiontobenegated.
Hereweuseanothercommonnotation,"cross"meansAND,"and"meansOR,and¬meansNOT.(Readersusingtext-onlybrowserswillseeLaTeXcodeinsteadofthewedgenotationtheyrepresent.)
HomomorphismandIsomorphism
BetweenBooleanalgebrasAandBThehomomorphismofisafunctionf:A→B,forallaandbinA:
f(ab)=f(a)f(b)
f(ab)=f(a)f(b)
f(0)=0
f(1)=1
ThenforallainA,f(¬a)=¬f(a)alsoholds.AllclassesofBooleanalgebra,togetherwiththeconceptofmorphism,formacategory.TheisomorphismfromAtoBisthebijectivehomomorphismfromAtoB.Theinverseofahomomorphismisalsoahomomorphism.WecallthetwoBooleanalgebrasAandBhomomorphism.FromthestandpointofBooleanalgebratheory,theyareindistinguishable;theydifferonlyinthesignsoftheirelements.
DerivativeTheory
BooleanRing
EveryBooleanalgebra(A,,)allleadtoaring(A,+,*),bydefininga+b=(a¬b)(b¬a)(Thisoperationiscalled"symmetricdifference"insettheoryandXOR(exclusiveOR)inlogic)anda*b=ab.Thezeroelementofthisringcorrespondsto0inBooleanalgebra;themultiplicationunitelementoftheringis1inBooleanalgebra.Thisringhasthepropertyofmaintaininga*a=aforallainA;aringwiththispropertyiscalledaBooleanring.
Conversely,ifaBooleanringAisgiven,wecanconvertitintoaBooleanalgebrabydefiningxy=x+y+xyandxy=xy.Becausethesetwooperationsaremutuallyinverse,wecansaythateachBooleanringinducesaBooleanalgebra,orviceversa.Inaddition,themappingf:A→BisahomomorphismofBooleanalgebraifandonlyifitisahomomorphismofaBooleanring.TheBooleanringandthecategoryofalgebraareequivalent.
TheidealofBooleanalgebraAisasubsetI.ForallxandyinI,wehavexyinI,andforallxandyinA,ForallawehaveaxinI.TheconceptofidealconformstotheconceptofringidealinBooleanringA.TheidealIofAiscalledprimeideal,ifI≠A;andifabinIalwaysimpliesainIorbinI.TheidealIofAiscalledthemaximalideal.IfI≠AandtheonlyidealthattrulycontainsIisAitself.TheseconceptsconformtotheringtheoryconceptsofprimeidealsandmaximalidealsinBooleanringA.
Theidealdualityisafilter.ThefilterofBooleanalgebraAisthesubsetp,forallx,yinpwehavexyinp,andforallainA,ifax=athenaisinp.
Howtorepresent
ItcanbeprovedthatallfiniteBooleanalgebrasareisomorphictotheBooleanalgebrasofallsubsetsofthisfiniteset.Inaddition,thenumberofelementsinallfiniteBooleanalgebrasisapoweroftwo.
Stone’sfamousrepresentationtheoremofBooleanalgebrastatesthatallBooleanalgebrasAareisomorphictoallBooleanalgebrasofclosedopensetsinacertain(compactandcompletelydisconnectedHausdorff)topologicalspace.
Axiomatization
In1933,theAmericanmathematicianEdwardVermilyeHuntington(1874-1952)demonstratedthefollowingaxiomatizationofBooleanalgebra:
:X+y=y+x.
Associationlaw:(x+y)+z=x+(y+z).
Huntingtonequation:n(n(x)+y)+n(n(x)+n(y))=x.
Theunaryfunctionsymbolncanbepronouncedas'complement'.
HerbertRobbinsthenposesthefollowingquestion:CantheHuntingtonequationbeshortenedtothefollowingequation,andthisnewequationtogetherwiththeassociativeandcommutativelawsbecomethebasisofBooleanalgebra?TheaxiomofRobbinsalgebra,thequestionbecomes:AreallRobbinsalgebrasBooleanalgebras?
AxiomizationofRobbinsalgebras:
Commutativelaw:x+y=y+x.
Associationlaw:(x+y)+z=x+(y+z).
Robbinsequation:n(n(x+y')+n(x+n(y)))=x.
Thisquestionhasbeenpublicsincethe1930sandhasbecomethefavoritequestionofAlfredTarskiandhisstudents.
In1996,WilliamMcCuneatArgonneNationalLaboratory,builtontheworkofLarryWos,SteveWinker,andBobVeroff,definitelyansweredthislong-standingquestion:AllRobbinsalgebrasareBooleanalgebra.ThisworkisdoneusingMcCune'sautomaticreasoningprogramEQP.
Rule
SubstitutionruleItcanbedescribedasanyvariableAinalogicalalgebraicformula,whichcanbereplacedbyanotherfunctionZ,andtheequationstillholds.
ThedualityrulecanbedescribedasforanylogicalexpressionF,ifthe“+”isreplacedby“*”,“*”isreplacedby“+”,and“1”isreplacedby“0”.","0"isreplacedwith"1",andtheoriginallogicpriorityisstillmaintained,thenthedualGoftheoriginalfunctionFcanbeobtained,andFandGaredualsofeachother.Wecanseethatthebasicformulasappearinpairs,andthetwoaredual.
Theinversionrulehastheoriginalfunctionandtheinversefunctioniscalledinversion(usingMorgan’slaw).
Wecandescribetheinversionruleasfollows:"*”isreplacedby“+”,“+”isreplacedby“*”,“0”isreplacedby“1”,and“1”isreplacedby“0”;theoriginalvariableisreplacedbytheinversevariable,theinversevariableisreplacedbytheoriginalvariable,longThenon-signaturemeansthatthenon-signatureoftwoormorevariablesremainsunchanged,andtheinversefunctionoftheoriginalfunctionisobtained.
Law
Thelawofcomplementarity:
Thefirstlawofcomplementarity:IfA=0,then~A=1,ifA=1,then~A=0Note:~A=NOTA
Thesecondcomplementaritylaw:A*~A=0
Thethirdcomplementaritylaw:A+~A=1
Doublecomplementaritylaw:/=//A=A
Commutativelaw:
ANDcommutativelaw:A*B=B*A
ORcommutativelaw:A+B=B+A
AssociativeLaw:
ANDAssociativeLaw:A=C*
ORAssociativeLaw:A+=C+
DistributiveLaw:
FirstDistributiveLaw:A*=+
Thesecondlawofdistribution:A+=*
Thelawoftautology:
Thelawofthefirsttautology:A*A=AIfA=1,thenA*A=1;ifA=0,thenA*A=0.Therefore,theexpressionissimplifiedtoA
Thesecondtautology:A+A=AIfA=1,then1+1=1;ifA=0,then0+0=0.Therefore,theexpressionissimplifiedtoA
Tautologywithconstants:
A+1=1
A*1=A
A*0=0
A+0=A
Thelawofabsorption:
Thefirstlawofabsorption:A*=A
SecondAbsorptionLaw:A+=A
Prototype
Thereisk
Operationson{0,1}canbeextendedbytruthtablesOut,select0and1asthetruevaluesfalseandtrue.Theycanbelistedinaunifiedandapplication-independentmanner,allowingustonamethemoratleastlistthemindividually.ThesenamesprovideconvenientabbreviationsforBooleanoperations.nThenameoftheelementoperationisa2-digitbinarynumber.Therearetwosuchoperations,youcan'tgetamoreconcisenomenclature!
Thefollowingshowsthepatternandassociatednamesofalloperationswithquantitiesfrom0to2.
TruthtableofBooleanoperationsupto2yuan
Constant
f0 | f1 |
0 | 1 |
Unaryoperation
x0 | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | |
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Binaryoperation
x0 | x1 | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | f8 | f9 | f10 | f11 | f12 | f13 | f14 | f15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Thesetablescontinuetohigheryuan,rightnTheelementhas2lines,eachlinegivesanevaluationorbindingofnvariablesx0,...xn−1,Andeachcolumnhasaheaderfi,whichgivestheithnelementoperationfi(x0,...,xn−1)Thevalueunderthisevaluation.Theoperationincludesthevariableitself,forexample,f2isx0andf10isx0(asitsunaryTwocopiesofthecounterpart)andf12isx1(thereisnoone-elementcounterpart).Negativeorcomplement¬x0appearsasf1appearsagainasf5,togetherwithf3(¬x1doesnotappearat1yuan),disjunctionorcombinationx0∨x1appearsasf14,Conjunctionorcrossingx0∧x1appearsasf8,whichimpliesx0→x1appearsasf13,XORorsymmetricdifferencex0⊕x1appearsasf6,thedifferencesetx0−x1appearsasf2andsoon.ForothernamesorrepresentationsofBooleanfunctions,pleaserefertozero-orderlogic.
Asasecondarydetailaboutitsformratherthanitscontent,analgebraicoperationistraditionallyorganizedasalist.HereweindextheoperationsofBooleanalgebrabyfiniteoperationson{0,1}.Theabove-mentionedtruthtableindicatesthesortingfirstaccordingtothenumberofyuan,andthenthelistofoperationsforeachnumberofyuan.Theorderofthelistofagivenelementnumberisdeterminedbythefollowingtworules.
(i)Therowiinthelefthalfofthetableisthebinaryrepresentationofi,withtheleastsignificantbitor0Itisatthefarleft(the"littleendian"orderwasoriginallyproposedbyAlanTuring,soitisnotunreasonablycalledtheTuringorder).
(ii)Isthecolumnjintherighthalfofthetablethebinaryrepresentationofj,orinlittleendianorder.Thesubscriptoftheoperationontheeffectisthetruthtableofthisoperation.
Applicationfield
Application
Booleanalgebracannotonlyimplementsetoperationsinthefieldofmathematics,Whichismorewidelyusedinlogicoperationsinthefieldsofelectronics,computerhardware,computersoftware,etc.:Whenthesetcontainsonlytwoelements(1and0),theycorrespondto{true}and{false},whichcanbeusedtoimplementlogicaloperations.Judgment.
Commonapplicationsinclude:
Digitalcircuitdesign,0and1correspondtothestateofabitinthedigitalcircuit,forexample:highlevel,lowlevelLevel.
Thecomputer'snetworksettingsusethebinarycharacteristicsofthecomputertoperformalogicalANDoperationbetweenthesubnetmaskandthelocalIPaddresstoobtainthecomputer'snetworkaddressandhostaddress.
DatabaseapplicationsrequirelogicaloperationstodeterminespecificquerytargetswhenqueryingthedatabasethroughSQLstatements.